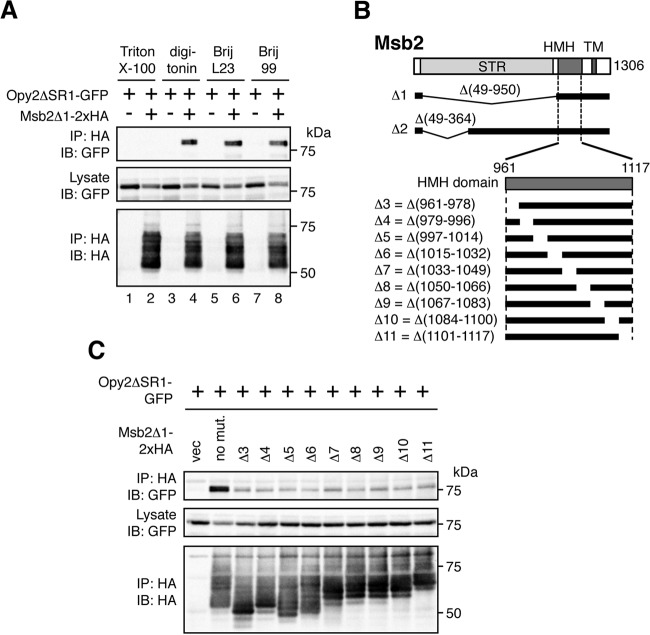
FIG 2.
Msb2 binds to Opy2. (A) Effect of detergent on Msb2-Opy2 binding. The yeast strain TM257 (a wild-type strain, except for the presence of nutritional markers) was cotransformed with expression plasmids for Opy2ΔSR1-GFP and Msb2Δ1-2×HA (+) or the vector control (−), both of which were under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Cells were grown in CARaf medium, and expression of the tagged Opy2 and Msb2 was induced by 2% galactose for 2 h. Cell lysates were prepared using buffer A containing the following detergents: 0.2% Triton X-100, 1.0% digitonin, 0.3% Brij L23, or 0.3% Brij 99. Msb2Δ1-2×HA was precipitated from cell lysates using an anti-HA antibody, and coprecipitated Opy2ΔSR1-GFP was probed with an anti-GFP antibody. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting. (B) Schematic model of Msb2. (Top) The full-length Msb2 molecule. The horizontal black bars represent the structures of Msb2 deletion mutants. (Bottom) An expansion of the HMH domain and its deletion mutants. STR, Ser/Thr-rich domain; HMH, Hkr1-Msb2 homology domain; TM, transmembrane domain. (C) The Msb2 HMH domain is necessary for Msb2-Opy2 interaction. The yeast strain KY562-1 (ssk2Δ ssk22Δ msb2Δ opy2Δ) was cotransformed with expression plasmids for Opy2ΔSR1-GFP and Msb2Δ1-2×HA (no mut., no mutation), the indicated deletion derivatives, or the vector control (vec), all of which were under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Cell growth, preparation of cell lysates, immunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting were as described in the legend to panel B. Buffer A containing 1.0% digitonin was used.