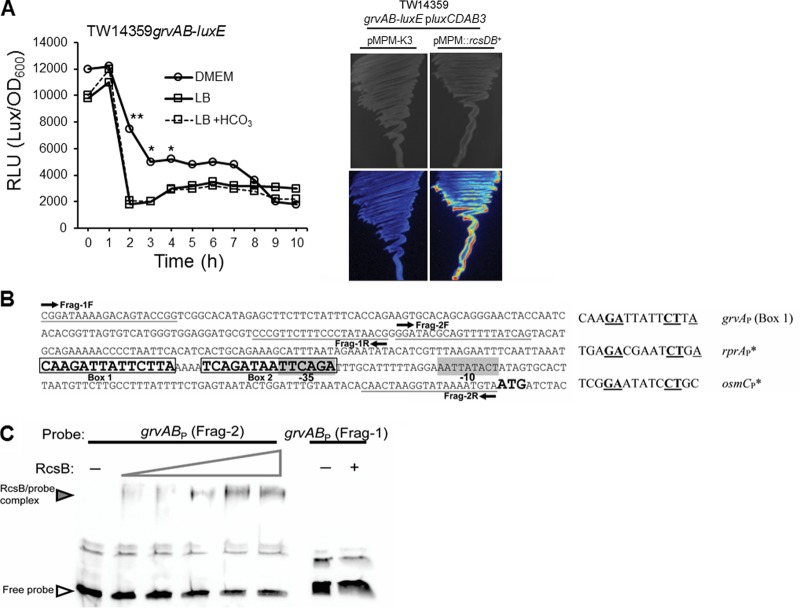
FIG 1.
Rcs response regulator RcsB directly activates transcription from the grvAB promoter. (A) (Left) Average luciferase activity (in relative light units [RLU]) plotted as a function of time for a single-copy grvAB-luxE fusion grown in DMEM, LB, or LB supplemented with 44 mM NaHCO3. Asterisks denote significance by Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; n ≥ 3). Plots at each time point did not vary from the mean by more than 5%. (Right) Growth and grvAB promoter expression (luciferase activity) (bottom) on LB agar plates for strain TW14359 grvAB-luxE/pluxCDAB3 transformed with empty vector pMPM-K3 (left) or pMPM::rcsDB (right). (B) (Left) Map of the grvAB promoter and flanking regions in strain TW14359. Fragments for EMSA (Frag-1 and Frag-2) and the respective primers for probe generation are indicated. Frag-1 is the negative control; Frag-2 contains two putative RcsB binding sites (Box 1 and Box 2). (Right) Alignment of box 1 from the grvAB promoter with experimentally proven RcsB homodimer boxes for rprA and osmC promoters. Conserved bases are in bold and underlined. (C) EMSA for RcsB binding to Frag-2 of the grvAB promoter. The wedge denotes the increasing amount of RcsB added (1 to 12 μg). For Frag-1 (control), RcsB was added at 0 μg (lane −) and 12 μg (lane +).