FIG 1.
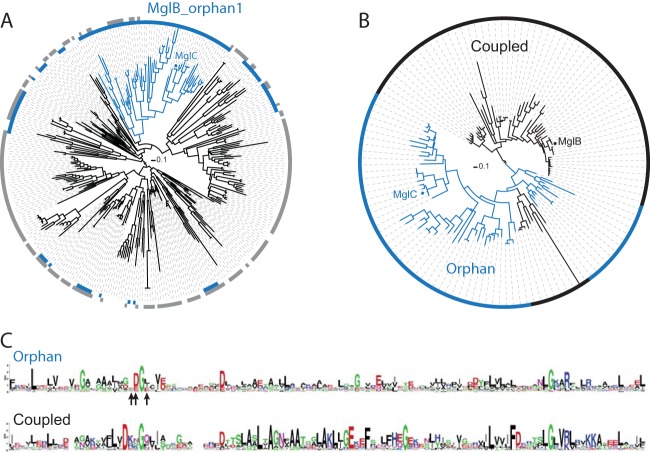
MglC is an orphan homolog of MglB. (A) Identification of the MglB_orphan1 subfamily. A phylogenetic tree was constructed from a multiple-sequence alignment of 328 orphan MglB sequences identified in a previous study (46). The innermost ring around the tree (blue) shows the sequences encoded in genomes that also encode group 1 MglA sequences, and the ring in gray shows the sequences encoded in genomes that encode group 2, 3, 4, or 5 MglA sequences. The blue branches identify the conserved MglB_orphan1 clade. (B) A phylogenetic tree built from a multiple-sequence alignment of members of the MglB_orphan1 clade and the MglB_coupled1 clade. Branches and ring colors identify the sequences from the MglB_orphan1 clade found in panel A (blue) and the MglB_coupled1 sequences that are genomically coupled to group 1 MglA (black). (C) Sequence logo corresponding to the clade composed entirely of coupled sequences and the clade composed of primarily orphan sequences (MglB_orphan1 sequences plus nine MglB_coupled1 sequences, as described in the text) were generated from the multiple-sequence alignment used in panel B that includes residues 15 to 129 of MglB (MXAN_1926) or residues 3 to 120 of MglC (MXAN_5770). Arrows below the orphan sequence logo indicate residues of MglC targeted for mutagenesis: F25, D26, and I28. In the logos, the letter size at each position represents the relative frequency of the given amino acid at that position.