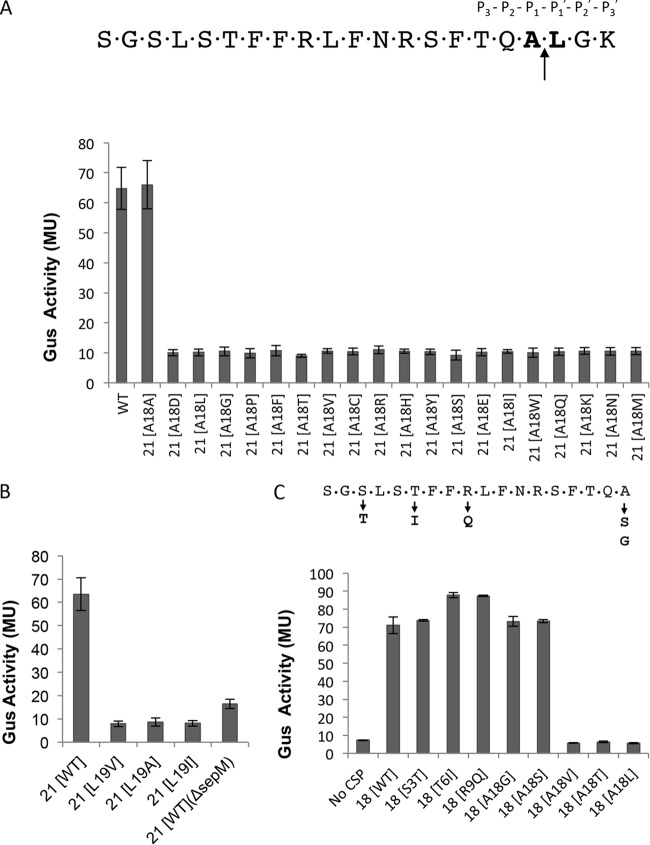
FIG 2.
SepM-mediated CSP-21 cleavage is highly site specific. The CSP sequence is shown with the conserved residues required for the generation of CSP-18. (A) Requirement for alanine at the 18th position. The 18th residue corresponding to the matured CSP was mutated to all possible 19 amino acids (the 18th and 19th residues are in bold). The constructs containing mutations were introduced into the ΔcomC strain (IBS-N42) carrying the reporter plasmid pIBN35 to produce endogenous CSP. β-Glucuronidase activity was measured at mid-exponential phase. (B) Requirement for leucine at the 19th position. The 19th residue corresponding to the matured CSP was mutated to alanine (L19A), valine (L19V), or isoleucine (L19I). The mutated constructs were introduced into the ΔcomC/pIBN35 strain to produce endogenous CSP, and β-glucuronidase activity was measured at mid-exponential phase. Wild-type (WT) CSP-21 served as a positive control, whereas the ΔsepM strain served as a negative control. (C) Verification of ComD activation by synthetic CSP-18 variants. Various synthetic CSP-18 peptides with substitutions at the 18th position were added to exponentially growing cultures of ΔsepM ΔcomC (IBS-N43)/pIBN35 cells, and β-glucuronidase activity was measured. Single amino acid substitutions shown below the CSP-18 sequence did not interfere with the activity. All experiments were repeated three times, and the means and standard deviations (error bars) are shown.