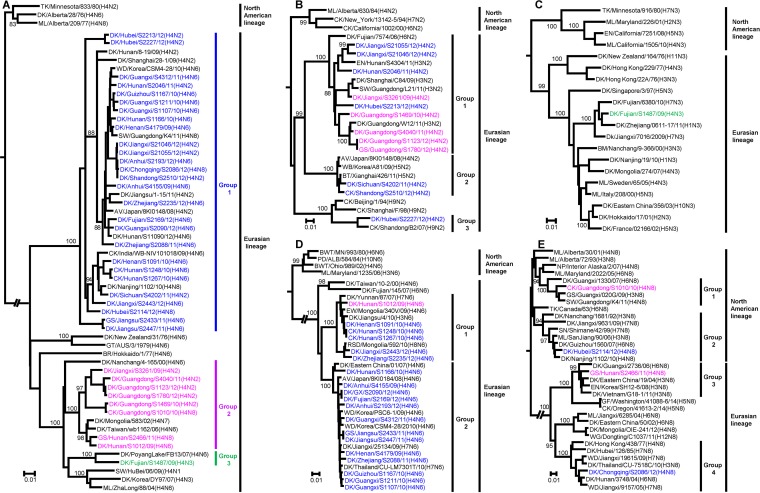
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic analyses of the HA and NA genes of H4 avian influenza viruses isolated from live poultry markets in China between 2009 and 2012. Phylogenetic trees were generated by using the neighbor-joining method and the MEGA5.0 software package. Neighbor-joining bootstrap values of ≥80 are shown at the major nodes of the phylogenetic trees. The regions of nucleotide sequences used for the phylogenetic analyses were the following: H4 HA, 20 to 1714; N2 NA, 20 to 1357; N3 NA, 19 to 1425; N6 NA, 40 to 1421; and N8 NA, 21 to 1433. The phylogenetic tree of the H4 HA genes was rooted to A/swine/Ontario/01911-1/99 (H4N6) (A), the N2 NA tree was rooted to A/blue-winged teal/Ohio/908/2002 (H3N2) (B), the N3 NA tree was rooted to A/black headed gull/Mongolia/1756/2006 (H16N3) (C), the N6 NA tree was rooted to A/duck/Wisconsin/480/1979 (H12N6) (D), and the N8 NA tree was rooted to A/mallard/Ohio/123/1989 (H6N8) (E). The viruses sequenced in this study are colored in the phylogenetic tree based on the phylogenetic classification of their HA genes: blue, magenta, and green for groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Abbreviations: AV, avian; BR, budgerigar; BWT, blue-winged teal; CK, chicken; DK, duck; EN, environment; EW, Eurasian wigeon; GF, gyrfalcon; GS, goose; GT, gray teal; MD, migratory duck; ML, mallard; NP, northern pintail; PD, pintail duck; RSD, ruddy shelduck; SN, swan; SW, swine; TK, turkey; WB, wild bird; WD, wild duck; WG, wild goose.