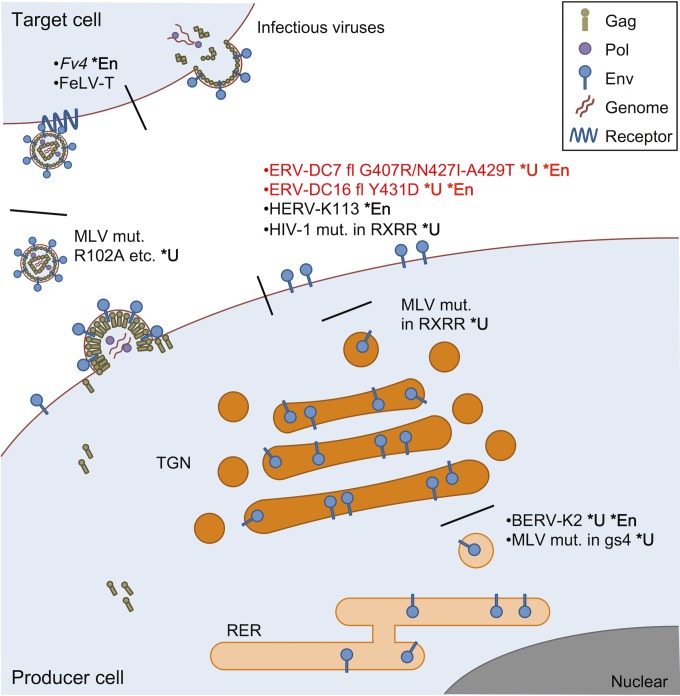
FIG 10.
Various Env dysfunctions caused by mutations within its SU. BERV-K2 Env and Fr-MLV Env mutants with mutations within glycosylation site 4 (gs4) are not cleaved because their mutation prevents intracellular trafficking from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) to the trans-Golgi network (TGN), where Env cleavage occurs (11, 63). Uncleaved Mo-MLV Env mutants with mutations within the cleavage motif (RXRR) are trapped in the TGN without transport to the cell surface (62). ERV-DC7 fl and ERV-DC16 fl, both of which are full length but harbor substitutions of G407R/N427I-A549T and Y431D, respectively, and Env mutants of HIV-1 with mutations within the cleavage motif are cleavage defective, and they can be transported to the cell surface but are not incorporated into virions (17). HERV-K113 Env can also reach the cell surface, but it cannot be incorporated into virions (68). Uncleaved Mo-MLV Env mutants with mutations within the N-terminal domain, such as R102A, are incorporated into virions, but they do not bind to viral receptors (64). Fv4 Env can be incorporated into virions and bind to viral receptors, but it does not undergo membrane fusion owing to a substitution in its TM fusion peptide (34, 69). FeLV-T Env is incorporated into virions and successfully binds its receptor, but it is unable to undergo fusion because of mutations within its PHQ motif, which mediates receptor binding and membrane fusion (70, 71). The defective fusion of FeLV-T Env is recovered by the presence of FeLIX (70). *U, uncleaved Env; *En, ERV Env.