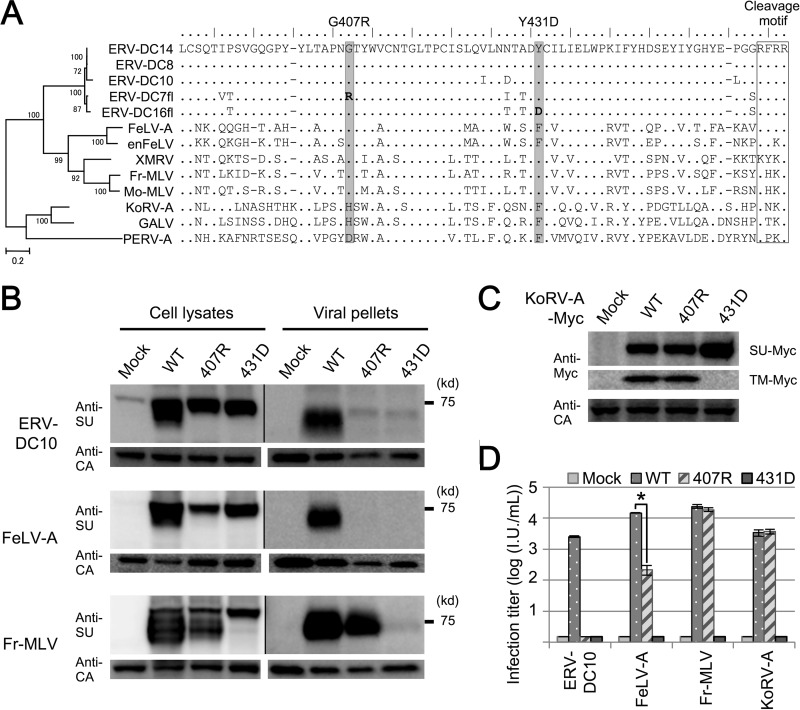
FIG 8.
Dysfunction caused by mutations within the SU C-terminal domain in gammaretroviruses. (A) A phylogenetic tree of Env in gammaretroviruses constructed by the maximum-likelihood method is shown on the left. The percentages of branch junctions indicate their bootstrap values (1,000 times). Amino acid sequences of the gammaretrovirus SU C terminus regions are also presented. The positions of G407R and Y431D are shaded. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of GP Lac cells expressing wild-type (WT) Env or the Env mutants described for panel A. We constructed expression plasmids for Env mutants of ERV-DC10, FeLV-A/Glasgow-1, and Fr-MLV/clone 57 and expressed them in GP Lac cells. After 48 h, we harvested the cell lysates and viral pellets from the culture supernatants and analyzed them. ERV-DC10 and FeLV-A Env were detected with an anti-FeLV SU antibody, and Fr-MLV Env proteins were detected with an anti-MLV SU antibody. Pr65 Gag precursor and Gag CA were detected with an anti-MLV CA antibody. The exposure time of the filter was different for the cell lysates and viral pellets. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of GP Lac cells expressing Myc-fused WT or mutant (407R or 431D) KoRV-A_1 Env. Lysates of these cells were harvested, and Env precursor-Myc and TM-Myc were detected with an anti-Myc antibody. Gag CA was detected with an anti-MLV CA antibody. (D) Infection assay using pseudotyped viruses of WT or mutant Env. Fresh HEK293T cells were inoculated with these viral supernatants, and after 48 h, X-Gal-positive cells were counted as infectious units (I.U.). *, P < 0.001 (Student's t test).