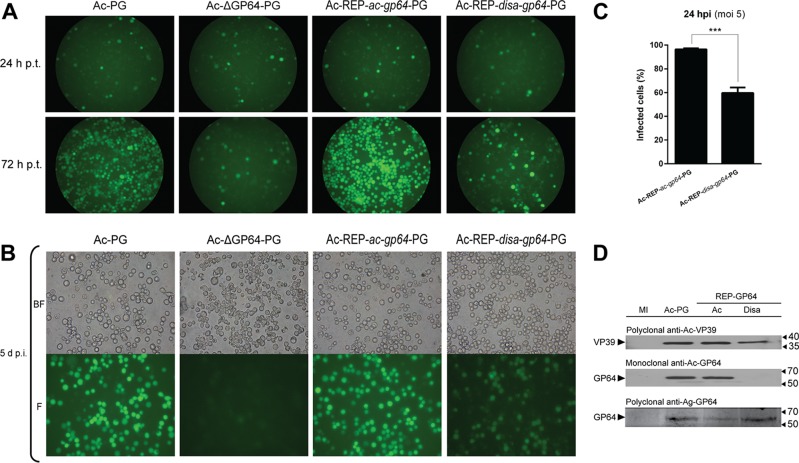
FIG 1.
Disa-GP64 is a functional envelope fusion protein. (A) Transfection assay of Ac-PG (used as a positive control); this is an AcMNPV bacmid containing both the polyhedrin [P] gene under the control of its natural promoter and the green florescence protein [G] gene under the control of the AcMNPV immediate early-1 gene promoter, Ac-ΔGP64-PG (negative control), Ac-REP-ac-gp64-PG (repaired virus), and Ac-REP-disa-gp64-PG (pseudotyped virus). A 1-μg volume of DNA from each virus was transfected into Sf9 cells. The cells were photographed at 24 and 72 h posttransfection (h p.t.). (B) Infection assay of transfection supernatants, Ac-REP-disa-gp64-PG transfection supernatant is infective to Sf9 cells. At 5 days posttransfection, clarified supernatants were used to infect Sf9 cells. The cells were photographed at 5 days postinfection (d p.i.). (C) The infection efficiency of the pseudotyped Ac-REP-disa-gp64-PG was reduced compared to that of the repaired Ac-REP-ac-gp64-PG. Cells were infected at an MOI of 5 (determined by endpoint dilution) and photographed at 24 h postinfection (hpi). (D) Disa-GP64 was detected only with a polyclonal antibody raised against GP64 of an alphabaculovirus (anti-Ag-GP64). Anti-Ac-VP39 antibody was used as a baculovirus infection control. Cells were mock infected (MI) or infected with (i) Ac-PG, (ii) Ac-REP-ac-gp64-PG (Ac), or (iii) Ac-REP-disa-gp64-PG (Disa) at an MOI of 5 for 72 hpi. Cells were harvested, and the total proteins were extracted, resolved on SDS-12% PAGE gels, and analyzed by immunoblotting with polyclonal anti-Ac-VP39, monoclonal anti-Ac-GP64, or polyclonal anti-Ag-GP64 antibody.