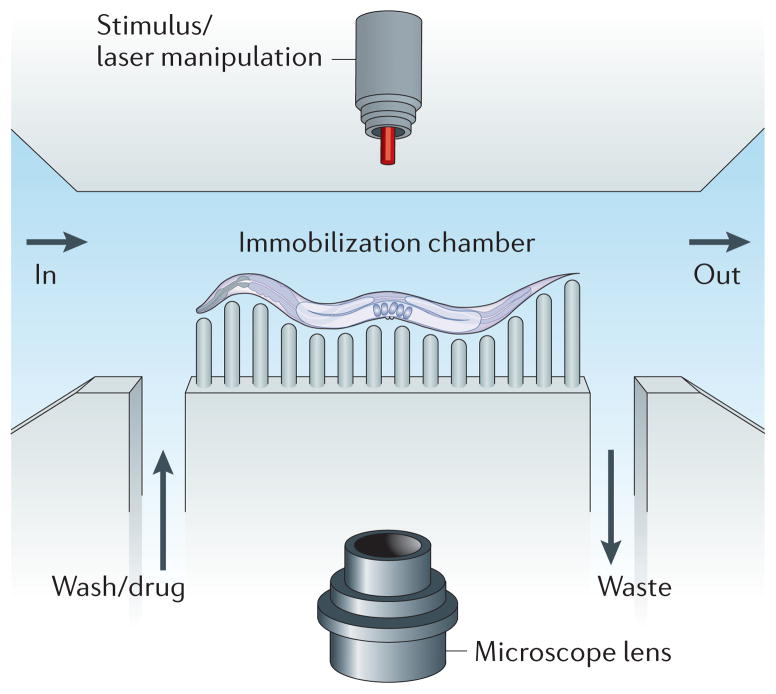
Figure 2. Caenorhabditis elegans microfluidics.
The basic layout for a worm microfluidic chamber consists of an inlet into the chamber (labelled ‘in’) and an outlet from the chamber (labelled ‘out’). A channel allows for input of media such as a wash solution or a drug. Another channel allows for the output of waste. Worms can be immobilized through many methods, including pressurization of a flexible polymer around the worm that restricts movement. A microscope can capture features of the worm for automated lifespan analysis or for longitudinal studies. Outside stimuli, such as laser manipulation, can also be added to the system.