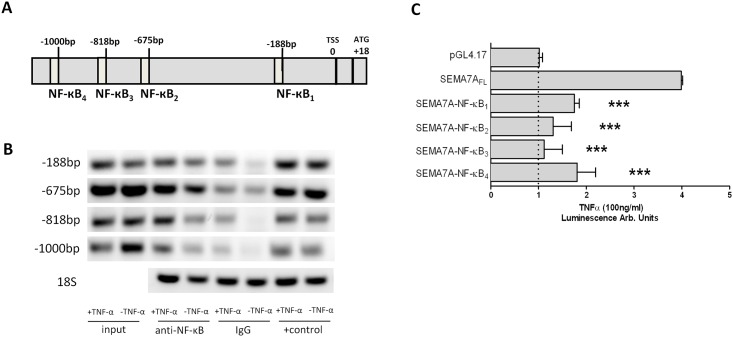
Fig 4. Role of NF-κB in the regulation of SEMA7A.
A) Graphic representation of the putative SEMA7A promoter. Four potential NF-κB binding elements were identified in the upstream sequence relative to the transcription start site (TSS). B) ChIP assay was employed to examine NF-κB binding to the human SEMA7A promoter in A549 monolayers after exposure to TNF-α. C) A549 cells were transfected with the SEMA7A reporter plasmid and site-directed mutation of each NF-κB binding site was performed. Empty reporter vector (pGL4.17) was used as a negative control and SEMA7A full length (SEMA7A-NF-κBFL) represents the SEMA7A promoter construct without site-directed mutation. All data are expressed as mean±SEM compared to SEMA7A-NF-κBFL, ***P < 0.001 as indicated, n = 3/ group, one representative blot of three is demonstrated).