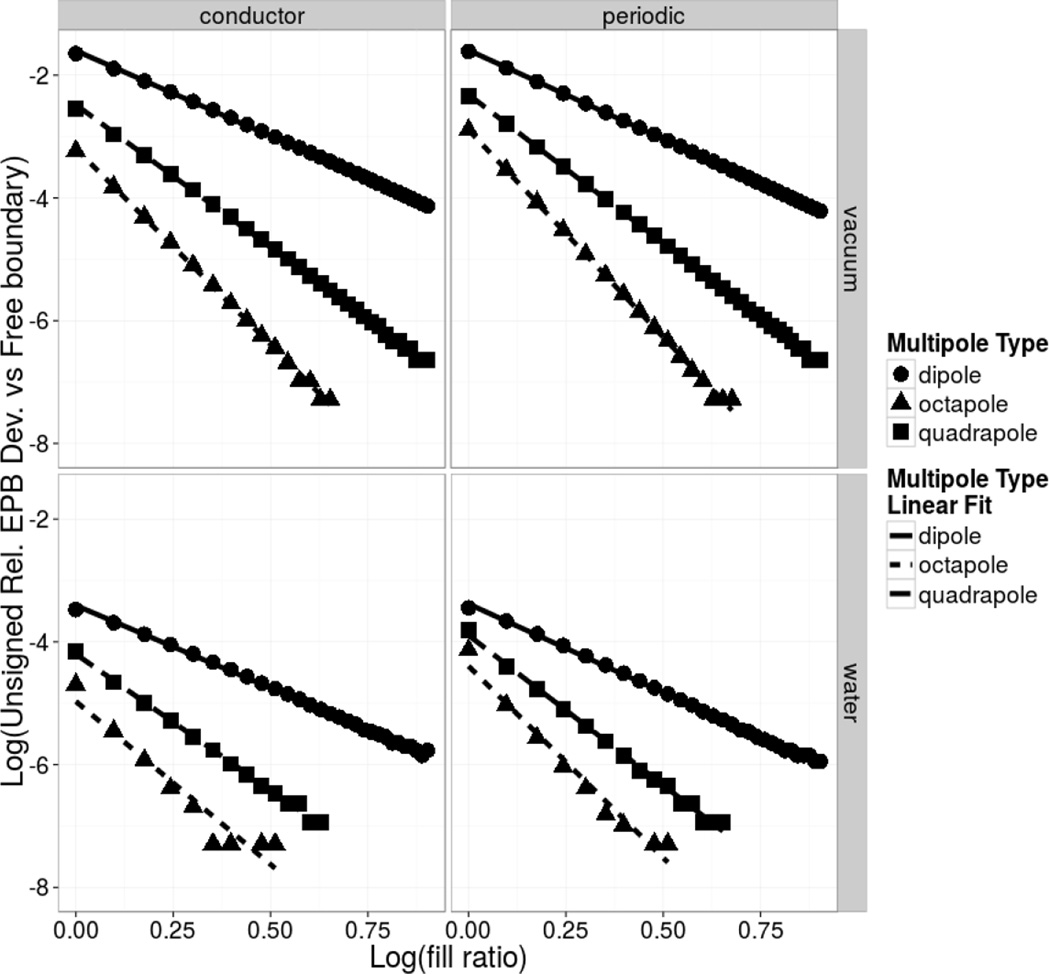
Figure 2. Differences between Electrostatic Energies by Different Boundary Conditions vs Fill Ratios.
Illustration of the grid-dimension dependence in deviations of electrostatic energies between the periodic/conductor boundary condition and the free boundary condition in vacuum (upper) and in water (lower) for three model systems: low dielectric spherical cavities with a radius of Angstrom imbedded with a dipole, quadrapole, or octapole, respectively. The dipole consists of unit positive and negative charges located at positive and negative .5 Å from the cavity center along the x axis. The quadrapole consists of four unit positive and negative charges located at the vertices of a unit square in the x–y plane and centered at the cavity center. The octapole consists of eight unit positive and negative charges located at the vertices of a unit cube centered at the cavity center. The program reports the sum of the Coulomb and reaction field energies as a single electrostatic energy.