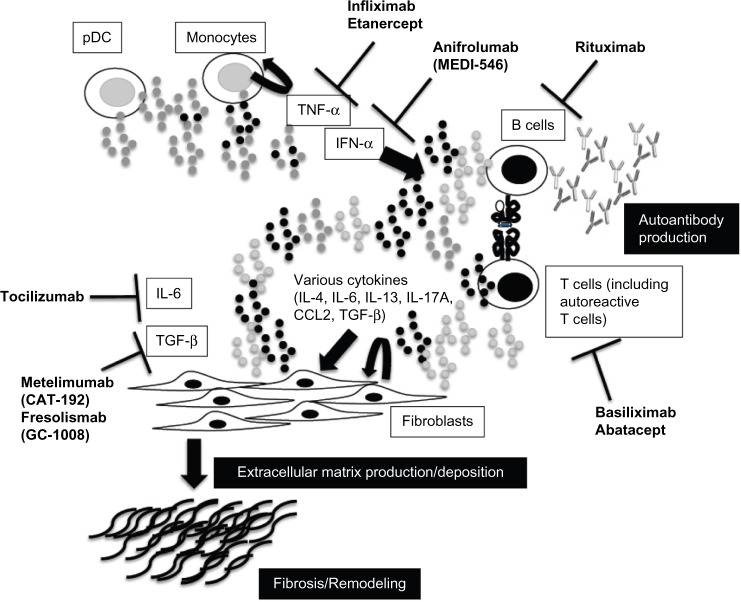
Figure 1.
Novel targets and treatment approaches for systemic sclerosis. Activation of fibroblasts and the production and deposition of extracellular matrix components are important in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. The release of various cytokines from activated lymphocytes plays a key role in fibroblast activation, and activated lymphocytes contribute to the production of autoantibodies. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) and/or monocytes activate lymphocytes through cytokines such as interferon (IFN) alpha. It might be possible to modify disease activity in patients with systemic sclerosis by regulating these targets.