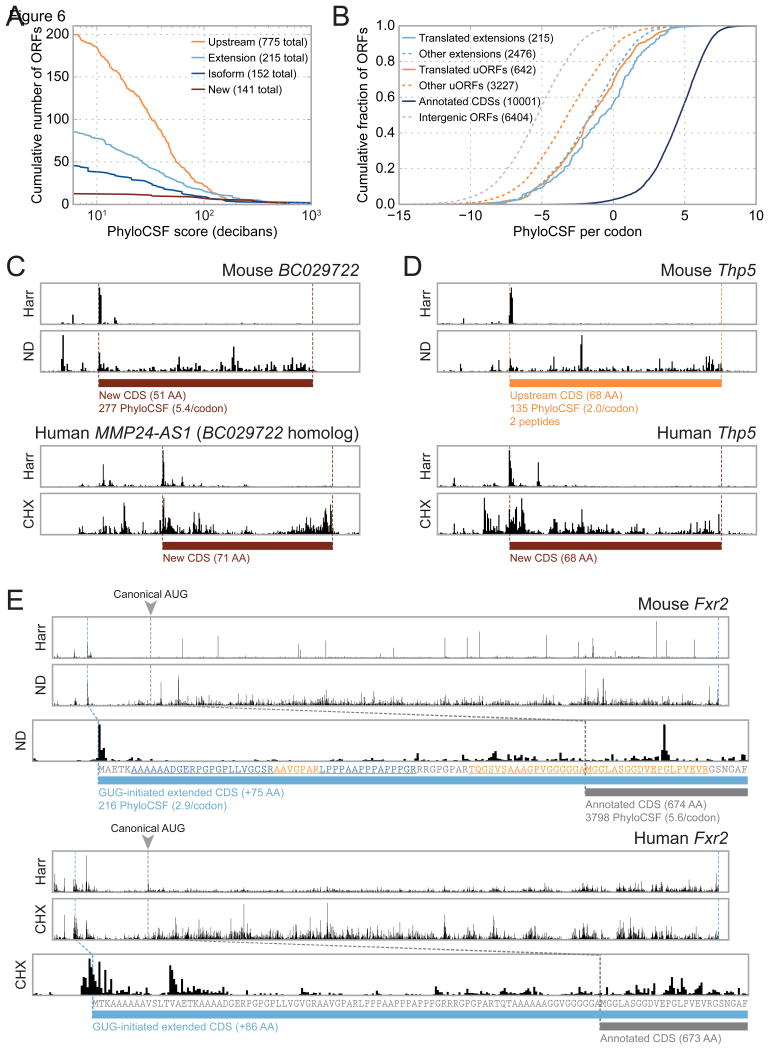
Figure 6. A significant subset of novel CDSs display signatures of codon-level conservation.
(A) For each threshold value, the number of novel CDSs of each type whose PhyloCSF score exceeds that threshold is plotted. PhyloCSF scores are calculated for only those codons non-overlapping with canonical CDSs. Scores indicate the log-likelihood that the ancestral locus was protein-coding; values of 10 or 20 correspond to 10:1 or 100:1 likelihood, respectively. The legend indicates the total number of ORFs for which a sequence alignment could be obtained, including those assigned negative PhyloCSF scores. (B) Cumulative distributions of per-codon PhyloCSF scores for translated uORFs and extensions of canonical CDSs. In both cases, PhyloCSF scores are significantly greater at translated CDSs relative to non-translated CDSs of the same type. Intergenic ORFs receive significantly lower scores and serve as negative controls. Because PhyloCSF scores vary linearly with the length of the sequence alignment, when comparing ORFs of different sizes, each score is normalized by the number of codons considered. See also Figure S3A. (C) RPF density at the mouse BC029722 (top) and human MMP24-AS1 (bottom) genes show translation of a previously unannotated CDS that is highly conserved phylogenetically. The multiple sequence alignment is shown in Figure S6A. A C-terminal eGFP fusion of human MMP24-AS1 was found to localize to the ER and Golgi apparatus (Figure S6B). (D) The Thp5 gene encodes a previously unannotated, conserved 68-amino acid protein in both mouse (top) and human (bottom). Two peptides from the mouse protein are identified by MS; full peptide and protein MS results are listed in Tables S2 and S3, and quality metrics are plotted in Figure S5. (E) Translation initiation of the Fxr2 gene occurs at an upstream GUG codon in both mouse BMDCs (top) and HFFs (bottom). In both cases, the canonical AUG initiation site appears to be unused. The translated region upstream of the canonical AUG appears to be highly conserved, and encodes multiple peptides detected by MS (peptide sequences highlighted in orange and blue). Translation initiation of Fxr2 via a GUG codon was confirmed via transient transfection with fluorescent reporter constructs (Figure S4B).