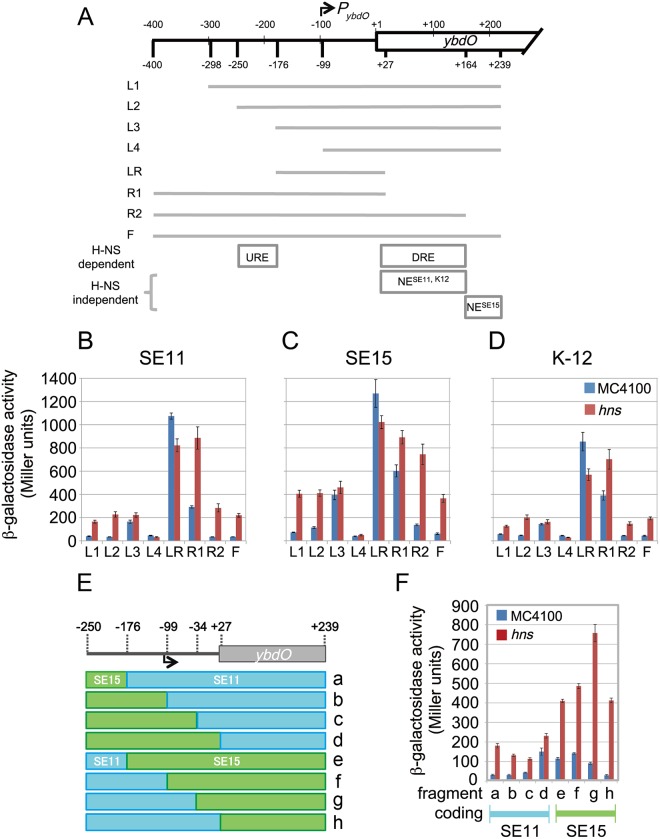
Fig 4. Comparison of the ybdO transcriptional activity in each of strains SE11, SE15, and K-12.
(A) Schematic representation of various lengths of DNA fragments carrying the ybdO regulatory region used in this analysis. The locations of the 5’ and 3’ ends of fragments are indicated by the distances from the ybdO start codon (the base numbers correspond to the nucleotide positions in K-12) with the transcriptional start site (TSS) of ybdO shown by an arrow indicating PybdO (top). The regions carried in each fragment (L1–F) are shown as gray lines (middle). The locations of the H-NS-dependent regulatory elements, URE and DRE, and H-NS-independent negative regulatory elements, NESE11, K-12 and NESE15, are indicated (bottom). (B–D) Comparison of the activities of SE11, SE15, and K-12 ybdO promoters as measured by β-galactosidase activity. The activity for each of the wild type (MC4100: blue bars) and hns mutants (MC4100 Δhns::km, hns: red bars) harboring pRW50 plasmids carrying the different ybdO promoter fragments (L1–F) of SE11 (B), SE15 (C), and K-12 (D) are indicated. The values represent the average of three independent assays. Standard errors are shown with error bars. (E) Schematic representation of hybrid fragments. Junction points are indicated above the upstream and coding regions of ybdO as nucleotide numbers relative to the initiation codon of ybdO in K-12. (F) Comparison of the transcriptional activities of the hybrid fragments as measured by β-galactosidase activity. β-galactosidase activity is shown for each of the wild type (MC4100: blue bars) and hns mutants (MC4100 Δhns::km, hns: red bars) carrying recombinant pRW50 plasmids containing the different hybrid fragments. The name (a ~ h) of each hybrid fragment (indicated at the bottom of the graph) corresponds to the name of the hybrid fragment in Fig 4E (indicated on the right of Fig 4E). The fragments are classified at the bottom of the panel as the fragment containing SE11 coding regions (pale blue bar) or SE15 coding regions (pale green bar).