Fig 5. Tumor Progression Following Immunization with Either Peptides or Rotating Lysates Prior to Tumor Challenge Consistently Resulted in Decreased Expression of Tumor MUC1 and MHC Proteins.
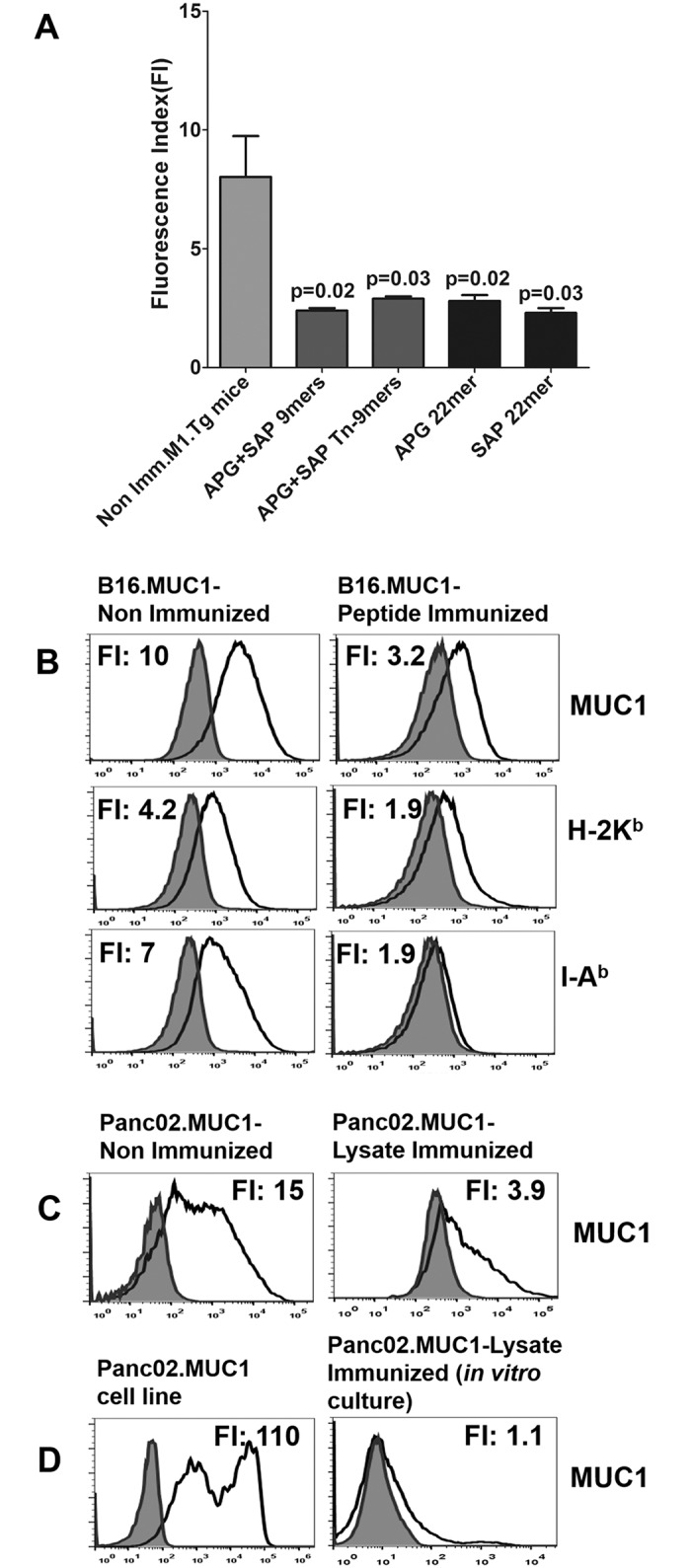
The resistant B16.MUC1 tumors that grew after peptide immunizations were excised, digested and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-CD45 APC-Cy7, anti-MUC1 FITC (CD227), anti-H-2Kb PE or anti-I-Ab PE. Cell surface MUC1 and MHC expression were significantly decreased following peptide vaccination compared to non-immunized mice. (A) Each bar represents the average fluorescent index (FI) of surface MUC1 expression for each treatment group. A typical experiment with n = 3 mice per group is shown; experiments were repeated at least 3 times. (B) Representative histograms are shown. The peptide shown is SAP 22mer, which is representative of the results for 9mer peptides. (C) Similar results were seen for Panc02.MUC1 in those groups where prior lysate immunization failed to prevent tumor outgrowth. (D) The cell line generated from Panc02.MUC1 tumor in vitro in G418 maintained low MUC1 surface expression when expanded (right panel) as compared to the parent cell line (D, left panel).
