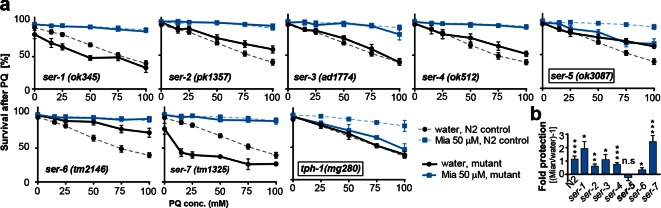
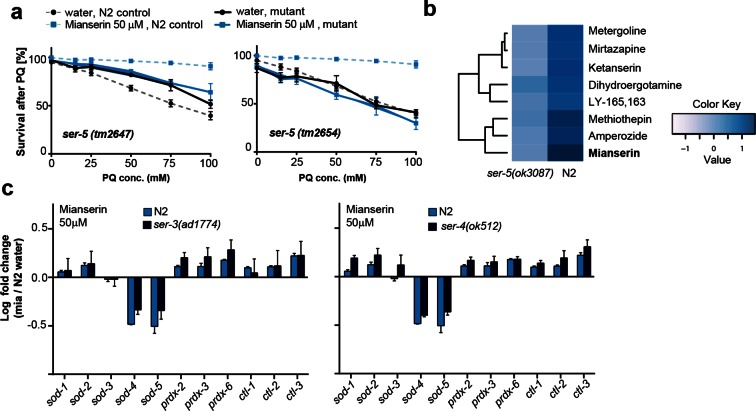
(
a) Survival of wt and two independent alleles of
ser-5 mutants,
ser-5(tm2647) or
ser-5(tm2654), treated with water or mianserin on day 1, followed by increasing concentrations of paraquat on day 5 of adulthood. (
b) Hierarchical clustering of fold change [serotonin antagonist/DMSO] in protection of wt (N2) and
ser-5 mutant animals, when treated with DMSO or serotonin antagonists on day 1 followed by paraquat on day 5, shows the degree of similarity in protection between 8 structurally different serotonin antagonists (left) and the requirement of
ser-5 for these antagonists to protect from oxidative stress. (
c) Bar graphs quantifying transcriptional drift by qRT-PCR (log fold-changes in gene expression) in 5-day-old N2 and
ser-3(ad1774) animals (left panel), and N2 and
ser-4(ok512) animals (right panel) treated with mianserin, relative to water-treated N2, determined by qRT-PCR. Mianserin treatment of
ser-3(ad1774) and
ser-4(ok512) strains result in a drift pattern, similar to those seen in N2. Thus, these receptors are neither required for drift-attenuation in redox genes, nor for the age-associated increase in oxidative stress resistance (
Figure 4). Error bars: S.E.M. For detailed statistics, see
Tables 6 and
7.