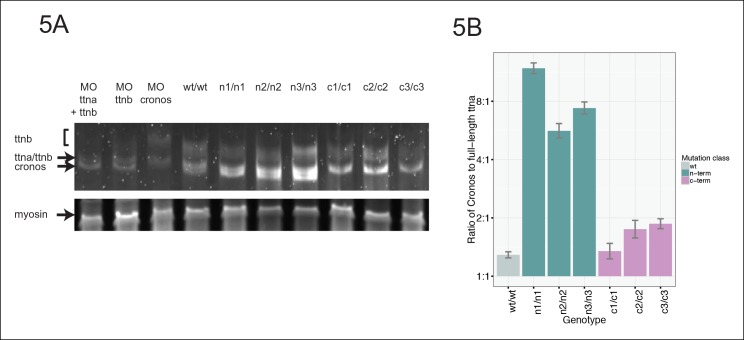
Figure 5. Premature termination codons in ttna differentially affect the levels of Cronos and full-length ttna depending on mutation location.
(A) 1.0% agarose gel reveals higher molecular weight bands corresponding to different splice isoforms of ttnb (all fish) and ttna (wild-type only). The arrow represents Cronos isoform of ttna, which is absent in C-terminal truncation mutants and in zebrafish treated with an ATG morpholino against this isoform. Ttna and ttnb expression results in a complex distribution of splice isoforms, whose identity and composition vary over early development (Steffen et al., 2007). (B) NMD results in a high ratio of Cronos to full-length ttna transcript levels in N-terminal but not C-terminal truncation mutants. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to estimate relative levels of the Cronos and full-length ttna trancripts for wild-type and mutant embryos. No efficiency difference was seen for the corresponding primer pairs.