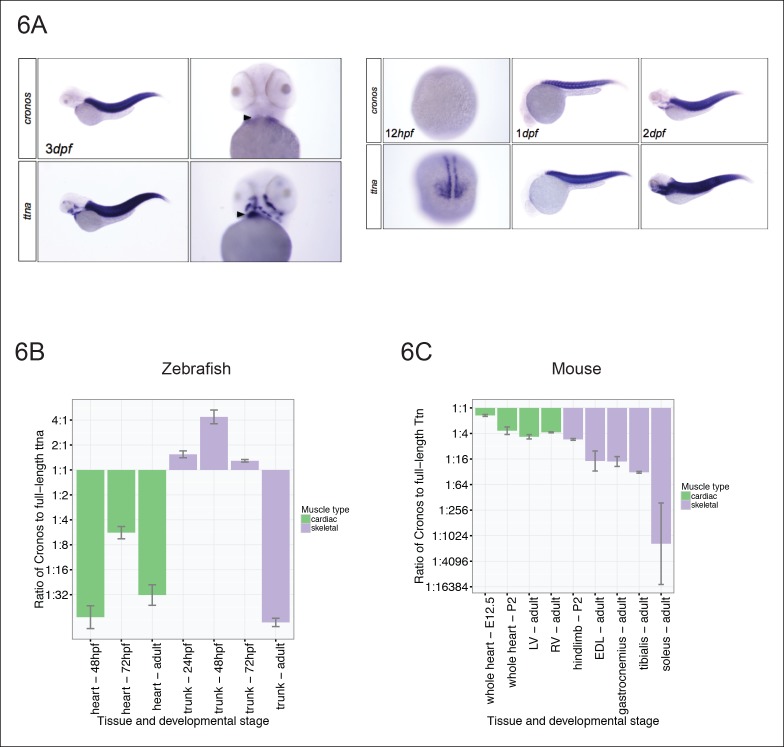
Figure 6. Tissue and developmental profile of Cronos and ttna expression in zebrafish and mouse heart and skeletal muscle.
(A) In situ hybridization at 72 hrpf (left) and 24 and 48 hpf (right) reveal prominent expression of both Cronos and full length ttna isoforms in zebrafish somites. In contrast, Cronos expression in developing zebrafish heart (arrow) is at low levels. (B) Quantitative PCR estimates of the ratio of Cronos to full-length ttna reveals prominent expression in developing zebrafish skeletal muscle, but markedly reduced expression in developing heart and in adult heart and skeletal muscle. (C) Quantitative PCR estimates of the ratio of Cronos to full-length Ttn reveals prominent expression in developing mouse hearts, which diminishes through development. Skeletal muscle Cronos expression is comparable in early postnatal mouse, but diminished in adulthood and varies by skeletal muscle bed. EDL = extensor digitorum longus. LV/RV = left/right ventricle.