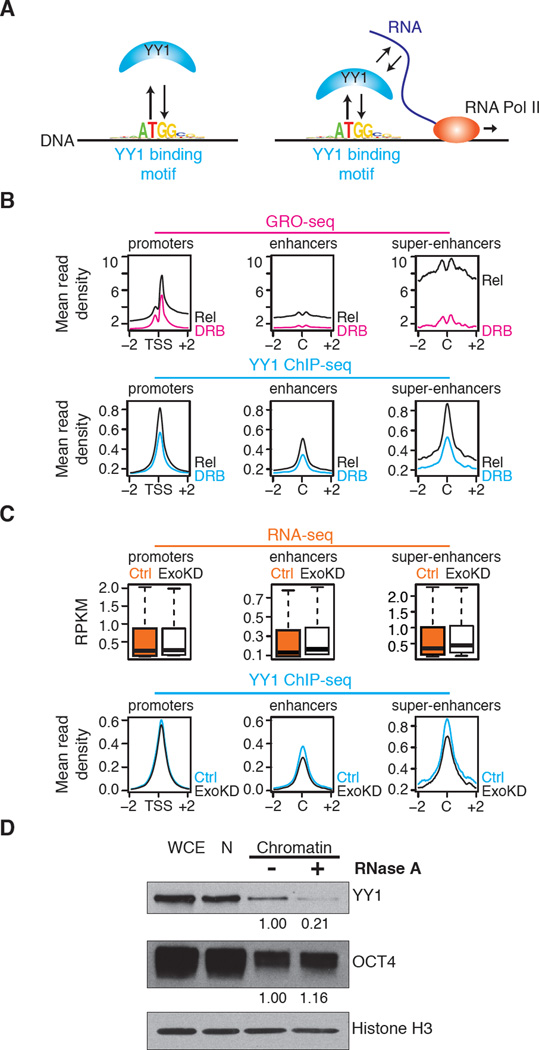
Fig. 3.
Perturbation of RNA levels affects YY1 binding to DNA. (A) Cartoon depicting hypothesis that RNA transcribed from regulatory elements enhances occupancy of these elements by TFs capable of binding both DNA and RNA. (B) (Top) GRO-seq reads (24) at promoters, enhancers, and super-enhancer constituents in cells before (DRB) and after release (Rel) from transcriptional inhibition by DRB. (Bottom) YY1 ChIP-seq reads at promoters, enhancers and super-enhancer constituents in cells before (DRB) and after release (Rel) from transcriptional inhibition by DRB. Increase in YY1 binding after release from DRB inhibition is significant: p-value < 3.6x10−207 for promoters, p-value < 1.6x10−214 for enhancers, p-value < 9.8x10−37 for super-enhancers. (C) (Top) Box plots depicting RNA-seq data for ribo-depleted total RNA at promoters, enhancers, and super-enhancers in ESCs after targeting with control (Ctrl) or Exosc3 (ExoKD) shRNA. (Bottom) Alignment of YY1 ChIP-seq reads at promoters, enhancers and super-enhancers in ESCs after targeting with control (Ctrl) or Exosc3 (ExoKD) shRNA. The decrease in YY1 binding in ExoKD ESCs is significant: p-value < 8.1x10−9 for promoters p-value < 1.8x10−27 for enhancers, p-value < 3.3x10−5 for super-enhancers. (D) Western blot analysis of YY1, OCT4, and histone H3 levels in whole-cell extracts (WCE), nuclei (N), and a nuclear chromatin preparation before and after RNase A treatment. Histone H3 serves as a loading control and OCT4 serves as a negative control. Quantitation of the relative levels of YY1 and OCT4 are noted.