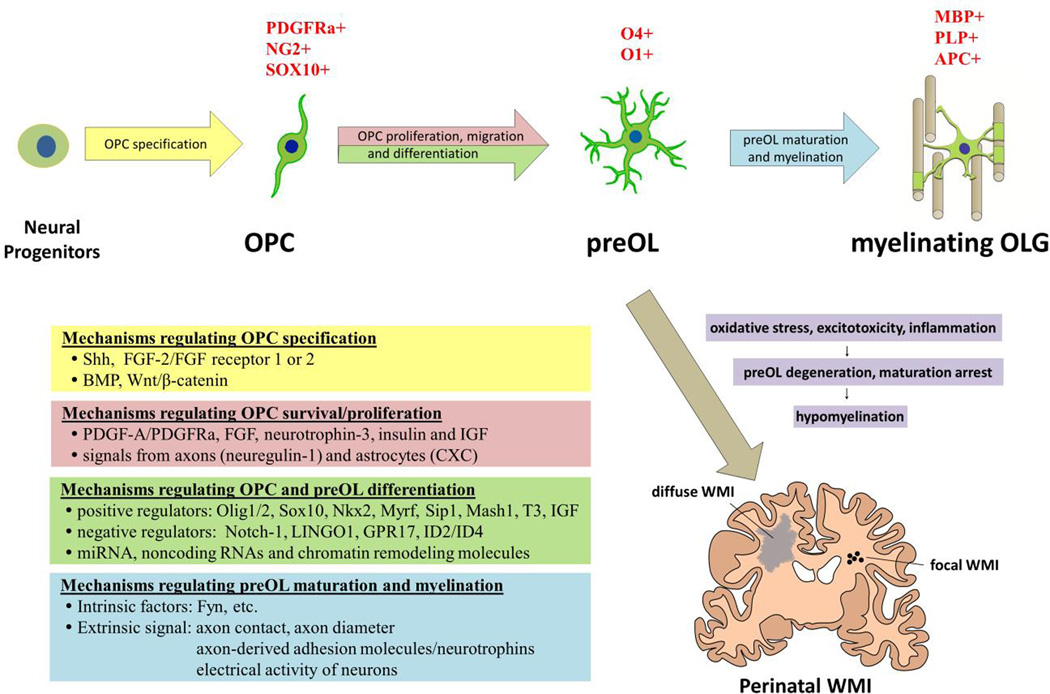
Figure 3. Major developmental phases of oligodendrocyte with the related regulatory mechanisms.
Schematic representation of oligodendrocyte lineage progression from oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPC) to premyelinating oligodendrocyte (preOL) and myelinating oligodendrocyte (OLG). The characteristic markers of each phase are shown on top of the cells. The mechanisms regulating each step of OLG development are summarized in the left table. PreOLs are selectively vulnerable to oxidative stress, excitotoxicity and inflammation. PreOL cell death and failure of maturation of regenerated preOLs are responsible for focal or diffuse white matter injury (WMI) associated with brain hypoxia-ischemia and infections in preterm and term infants. IGF: insulin-like growth factors; Myrf: myelin regulatory factor; Sip1: Smad interacting protein-1; LINGO1: leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin domain containing1; GPR17: G-protein-coupled receptor 17.