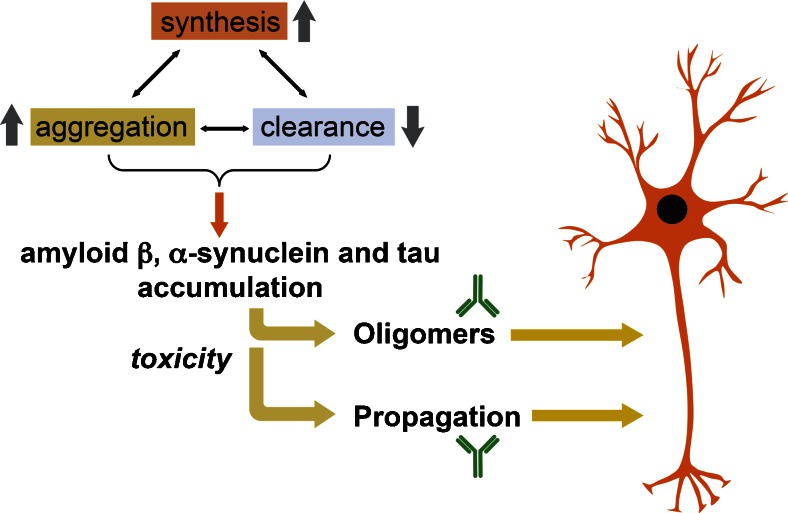
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of action of immunotherapy for neurodegenerative disorders. The misfolding and accumulation of amyloid-β, α-synuclein, and tau has been associated with an imbalance in the levels of their synthesis, aggregation, and clearance. The toxicity of these proteins is correlated with their ability to adopt specific conformations (oligomers, protofibrils) and to propagate from cell to cell, leading to neurodegeneration. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies may require reducing the synthesis, preventing the aggregation and/or enhancing the clearance of amyloid-β, α-synuclein, and tau. Specifically, immunotherapeutic approaches are able to target specific conformational species and inhibit cell-to-cell propagation of these proteins