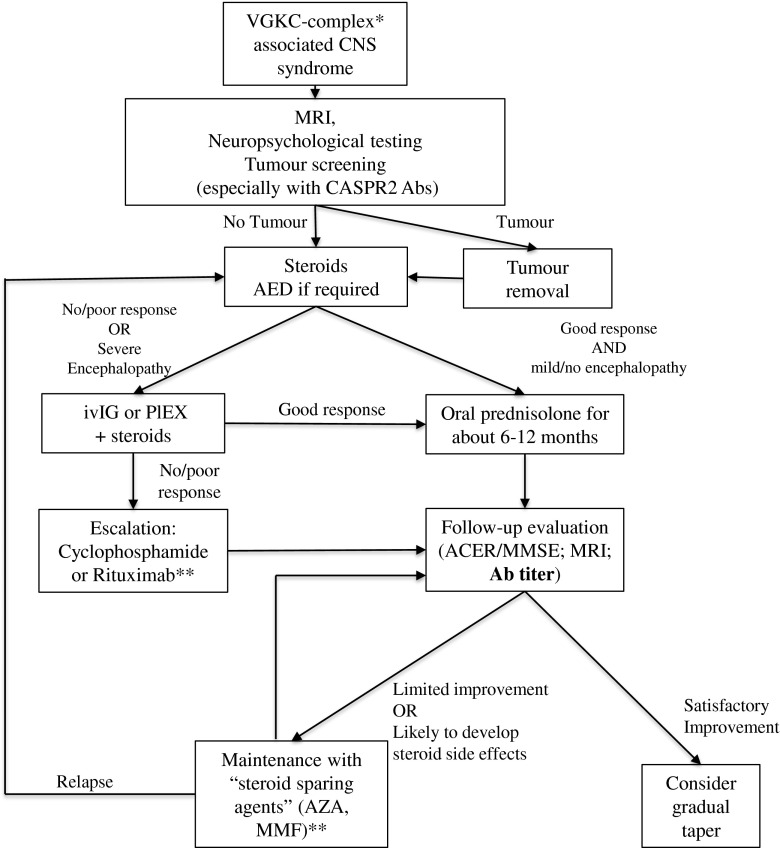
Fig. 3.
Management of voltage-gated potassium channel (VGKC) complex-associated disease. The algorithm describes a management approach to patients with central nervous system (CNS) syndromes and the presence in serum or cerebrospinal fluid of Abs directed against the VGKC complex, and it is intended as a general indication. Single patients could need a tailored approach based on the clinical phenotype *Mainly leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 and contactin-associated protein like 2 (CASPR2) **The efficacy of different immunosuppressants has never been tested systematically in autoimmune encephalitis, and previous evidence suggests, for example, a better efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) than cyclophosphamide in other autoimmune diseases [102]. Hence, the division between “escalating” and “steroid-sparing” drugs is not clear-cut and different strategies could be applied in different clinical settings MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; AED = antiepileptic drugs; IVIg = intravenous immunoglobulin; PLEX = plasma exchange; ACER = Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised; MMSE = Mini-mental State Examination; AZA = azathioprine