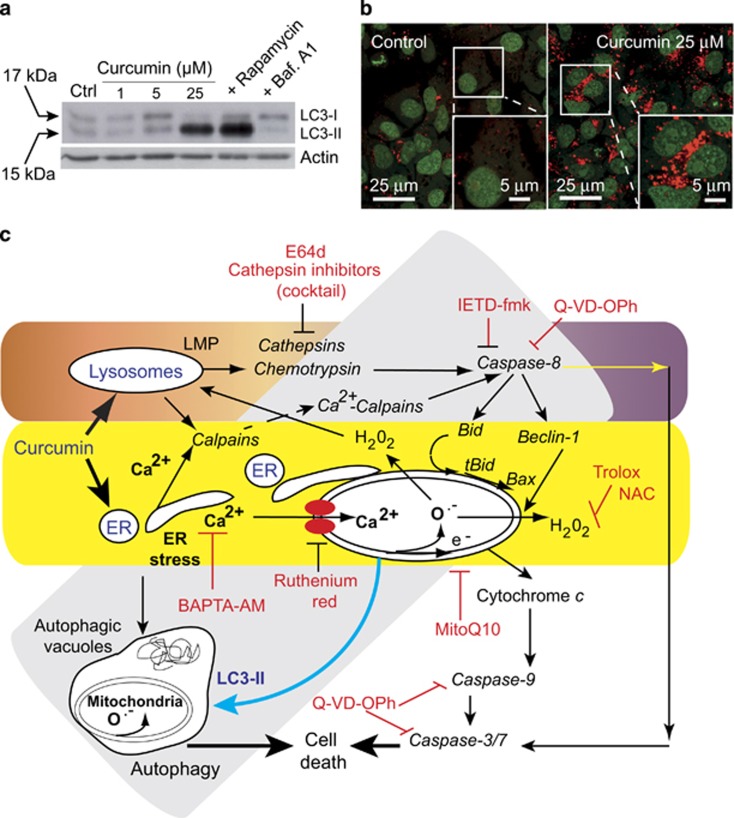
Figure 1.
(a) Western blot analysis of the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II in cells treated for 24 h with different curcumin concentrations (1, 5 or 25 μM). Control are: treatment of the cells with rapamycin 1 μM to induce autophagy and treatment with bafilomycin A1 0.5 μM to inhibit it. (b) Confocal microscopy of acridine orange (AO)-stained vesicles in cells treated with curcumin at 25 μM compared with the control. In the section showing cells treated with 25 μM curcumin, the enlarged panel (lower right panel) reveals the massive accumulation of AO-positive big vesicles with an acidic content that are remisniscent of autophagosomes. (c) Curcumin mainly targets the endoplasmic reticumum (ER) and lysosomes. The classic apoptotic pathway is mediated by calcium release from the ER. Uptake of this calcium by mitochondria disrupts mitochondrial homeostasis. Calcium alters mitochondrial electron transport causing substantial ROS production (both superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide), which leads to the opening of the permeability transition pore in the mitochondrial membrane. Consequently, cytochrome c is released and the caspase-9 and caspase-3/7 pathway is activated leading to cell death. Furthermore, the ER stress pathway leads to the formation of autophagic vacuoles that attempt to eliminate the dysfunctional mitochondria. The cleavage of Beclin-1 is associated with early apoptosis and leads to the accumulation of autophagic vacuoles. So, despite the activation of autophagy, cells undergo a type of ‘necrotic cell death' following these initial apoptotic events. These two pathways are parralled by a lysosomal pathway. Indeed, curcumin destabilizes lysosomal membranes leading to lysosomal membrane permeability and the activation of both cathepsins and chemotrypsins. Activated caspase-8 leads to Beclin-1 cleavage that inhibits the primarily induced autophagy. The increase in cytosolic calcium concentration also activates calpains that contribute to the degradation process and accelerate cell death. The various inhibitors used in this work are indicated at the place where the pathways are affected