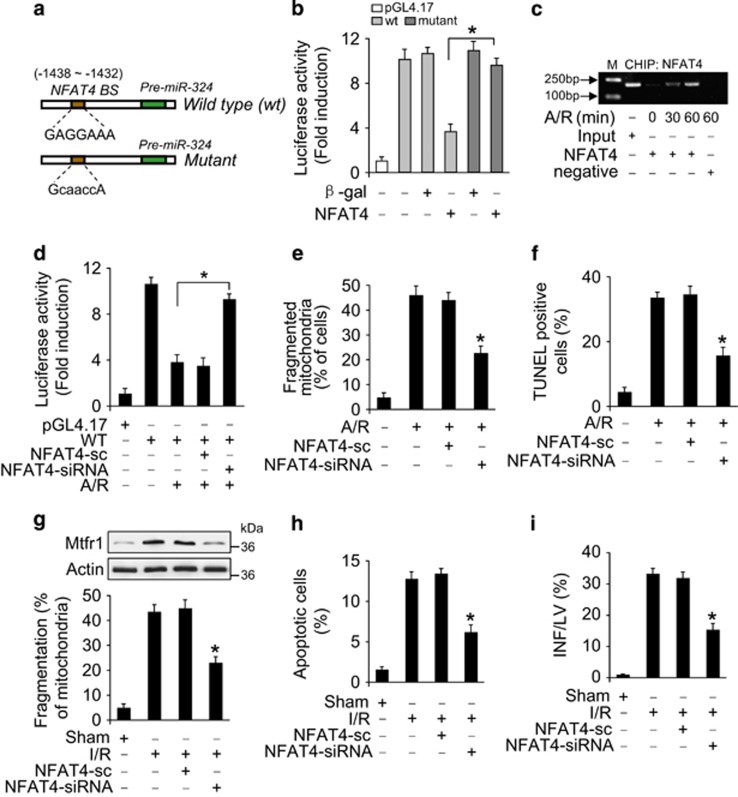
Figure 6.
miR-324-5p is a transcriptional target of NFAT4. (a) Mouse miR-324-5p promoter region contains a potential NFAT4 binding site. (b) NFAT4 attenuates miR-324-5p promoter activity. Cardiomyocytes were treated with the adenoviral β-gal or NFAT4, the constructs of the empty vector (pGL-4.17), the wild-type promoter (wt) or the promoter with mutations in the binding site (mutant), respectively. Luciferase activity was assayed. *P<0.05. (c) ChIP analysis of NFAT4 binding to the promoter of miR-324-5p. (d) Knockdown of NFAT4 inhibits the decrease of miR-324-5p promoter activity induced by A/R. Cardiomyocytes were treated with the adenoviral NFAT4-siRNA or NFAT4-sc, the constructs of the empty vector (pGL-4.17), the wt promoter, then were treated with A/R. Luciferase activity was assayed. *P<0.05. (e and f) Knockdown of NFAT4 reduces mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. Cardiomyocytes were infected with adenoviral NFAT4-siRNA or NFAT4-sc, and then exposed to A/R, mitochondrial fission (e) and apoptosis (f) were analyzed. *P<0.05 versus A/R alone. (g and h) Knockdown of NFAT4 attenuates mitochondrial fission and apoptosis upon I/R. After intracoronary delivery of adenoviruses harboring NFAT4 siRNA or the scrambled form, the mice were subjected to I/R injury. Mtfr1 levels were analyzed by immunblot (g, upper panel). Mitochondrial fission (g, lower panel) and apoptosis (h) were analyzed. *P<0.05 versus I/R alone. (i) Knockdown of NFAT4 decreases myocardial infarct sizes in response to I/R. Mice were treated as described for (g), and infarct sizes were calculated. *P<0.05 versus I/R alone