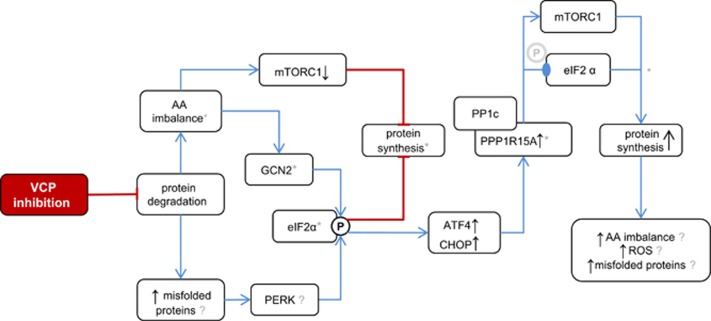
Figure 6.
Proposed working model of the mechanisms by which VCP inhibitors induce cancer cell death. VCP inhibition impinges on protein degradation, resulting in aberrant amino acid (AA) recycling and increased levels of misfolded proteins in the ER. This results in reduced mTORC1 activity and activates the eIF2α kinases EIF2AK4 (GCN2) and EIF2AK3 (PERK), thereby attenuating protein synthesis to alleviate proteotoxic stress. Downstream of eIF2α, the ATF4/CHOP-mediated induction of PPP1R15A governs eIF2α dephosphorylation by PPP1R15A/PP1c and increases mTORC1 activity. Together, these effects promote protein synthesis, resulting in inadequate attenuation of protein translation that aggravates cell stress and death through mechanisms that may involve amino acid imbalance, reactive oxygen species, and ER stress caused by misfolded proteins.  Phosphorylated serine 51;
Phosphorylated serine 51;  dephosphorylated serine 51; *probable qualitative or quantitative differences between VCP and proteasome inhibitors
dephosphorylated serine 51; *probable qualitative or quantitative differences between VCP and proteasome inhibitors