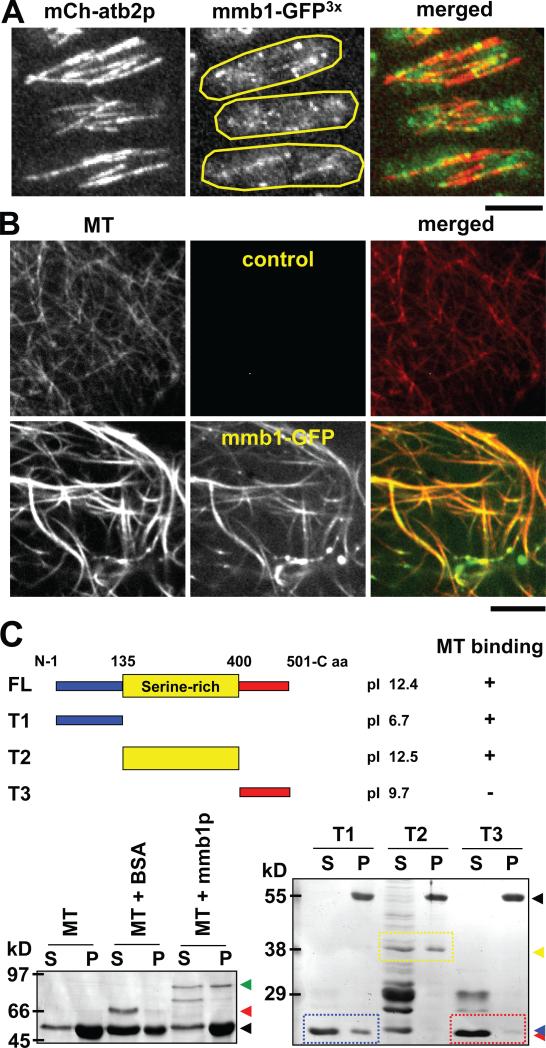
Figure 1. Mmb1p is a microtubule binding protein.
(A) Images of a wildtype cell expressing mCherry-atb2 and mmb1-GFP. Shown are maximum-projection images of three interphase cells. Mmb1-GFP appears as dots or short bars decorating the microtubule lattices. Bar, 5 μm. (See also Fig. S1A)
(B) In vitro microtubule binding assay. Taxol-stabilized microtubules (MT) (red) were polymerized from porcine brain tubulin decorated with Alexa Flour® 594 dye. Recombinant His-GFP-mmb1p (green) was isolated from E. coli. Image shows mmb1-GFP decorating the microtubule lattices and bundling microtubules. Bar, 5 μm.
(C) In vitro microtubule co-sedimentation assay. Cartoon shows full length mmb1p and different truncations and their predicted isoelectric points pI. First gel shows mmb1p full length interaction with microtubules (MT). Mixtures of taxol-stabilized microtubules (MT) and BSA or His-GFP-mmb1p were centrifuged, and the supernatants (S) and pellets (P) were analyzed by gel electrophoresis and coomassie blue staining. Control MT and MT+BSA lanes show little or no co-sedimentations with the microtubule pellets (position of tubulin, black arrow head; position of BSA, red arrow head). The MT+mmb1p lane shows co-sedimentation of mmb1p and microtubules (position of mmb1p, green arrow head). Some Mmb1p and degradation products remain in the supernatant. Second gel maps the interaction domains of mmb1p with microtubules. Different truncated mmb1p versions were tested for microtubule binding (tubulin, black arrow head): the N-terminal T1 domain (position of T1, blue arrow head), middle serine-rich T2 domain (position of T2, yellow arrow head), and C-terminal T3 domain (position of T3, red arrow head). Both T1 and T2 show co-sedimentations with the microtubule pellets. T3 remains in the supernatant. (See also Fig. S1B and Fig. S2)