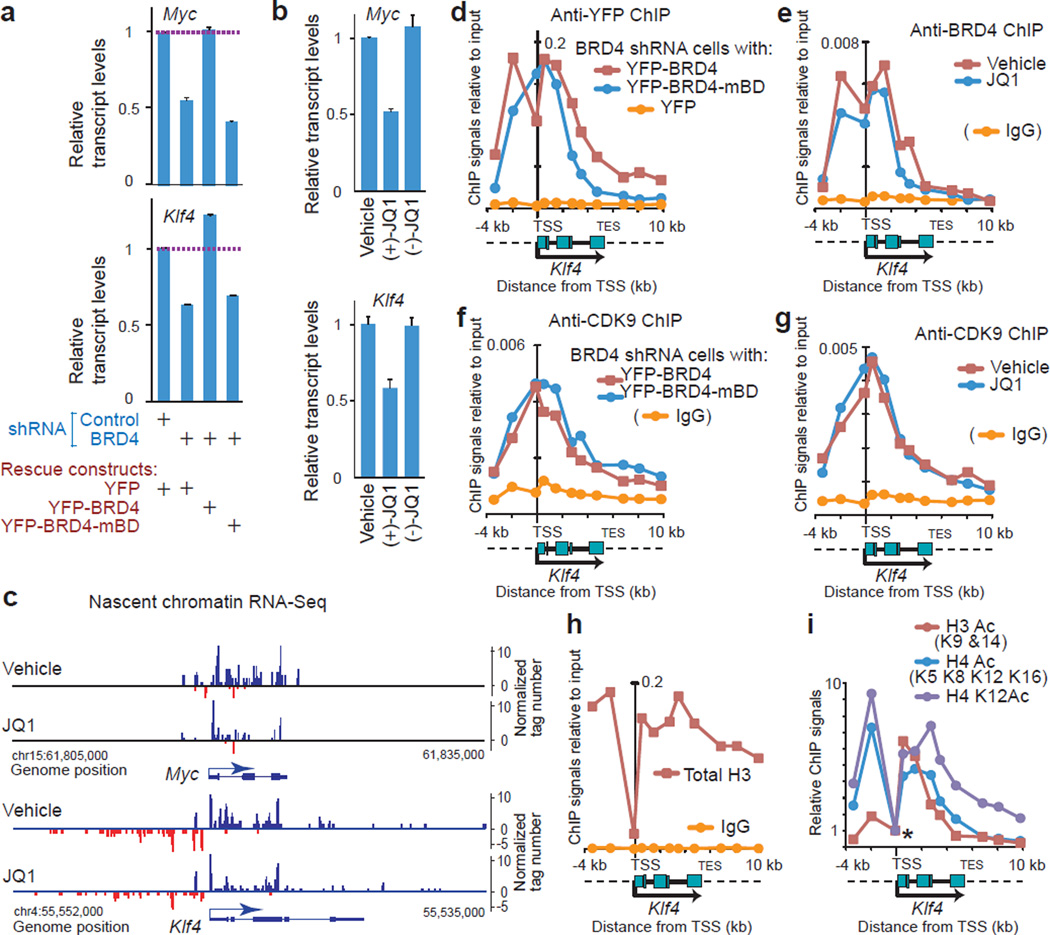
Figure 4. BD-mediated interaction with acetylated histones was required for BRD4-dependent expression of Myc and Klf4 but not for the recruitment of BRD4 and P-TEFb at the TSS.
(a, b), Myc and Klf4 expressions in BRD4 knockdown cells reconstituted with the rescue constructs indicated (a) and NIH3T3 cells treated with JQ1 stereoisomers (1 µM, 2 h) or vehicle (DMSO) (b), detected by qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to Gapdh and represent means ± s.e.m. (n = 3 technical replicates.) c, Genome browser views of strand-specific chromatin-bound RNA-seq reads across the Myc and Klf4 gene loci in NIH3T3 cells treated with JQ1 (500 nM, 1 h) or vehicle (DMSO). (d, f), ChIP-qPCR assays demonstrating binding of BRD4 (d) and CDK9 (f) on the Klf4 gene locus (from −4 kb to +10 kb relative to the TSS) in BRD4 knockdown cells expressing YFP-BRD4 proteins (wild type or mBD mutant) or YFP alone. Signals relative to input DNA (y-axis) are plotted against genomic positions of PCR primers (x-axis). Dotted lines in the diagram of the Klf4 gene locus represent the flanking regions. Background signals (yellow lines) were assessed in cells expressing YFP-alone (d) or using normal rabbit IgG (f). (e, g) ChIP-qPCR assays demonstrating binding of BRD4 (e) and CDK9 (g) on the Klf4 gene locus in cells treated with JQ1 (1 µM, 2 h) or vehicle (DMSO). (h, i), ChIP assays using anti-histone antibodies indicated. In i, ChIP signals were normalized, relative to the signals at the TSS (marked by an asterisk).