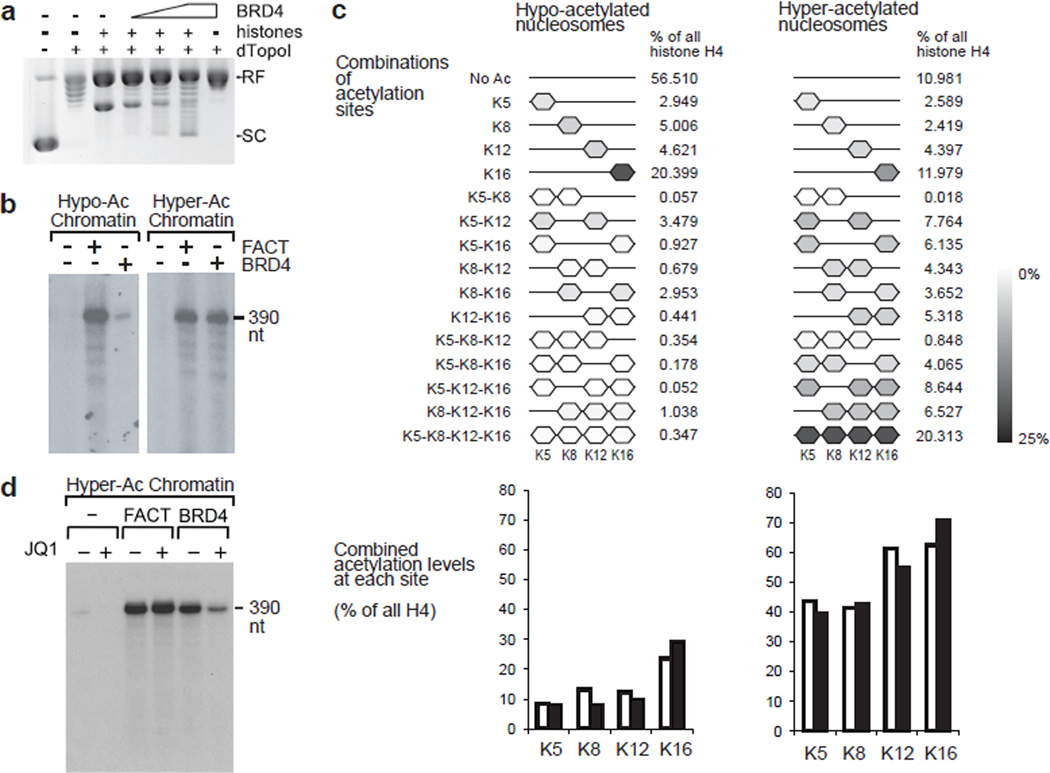
Figure 5. BRD4 possesses a histone chaperone activity and assisted elongating Pol II to transcribe through hyperacetylated nucleosomes in vitro.
a, In vitro plasmid supercoiling assays. RF indicates the position of circular plasmid DNA relaxed in the presence of Drosophila topoisomerase I fragment ND423 (dTopoI). SC indicates the position of supercoils introduced by hyperacetylated core histones (6 pmoles) and BRD4 (1, 2.5, and 5 pmoles). (b-d) The effects of BRD4 and the FACT complex on in vitro transcription of hypo- and hyper-acetylated chromatin templates (b), and the effects of JQ1 on transcription of hyper-acetylated chromatin template (d). Labeled RNA was resolved on 10% polyacrylamide urea gels. c, Relative quantification of H4 acetylations by quantitative mass spectrometry in the hypoacetylated and hyperacetylated histones used in reconstituted transcription assays. Results of two independent experiments. For the display of combinations of acetylated sites, means of two experiments are shown. For combined acetylation levels at each acetylation site, individual results are shown by open and filled bars. Uncropped images of the blots are shown in Supplementary Data Set 1.