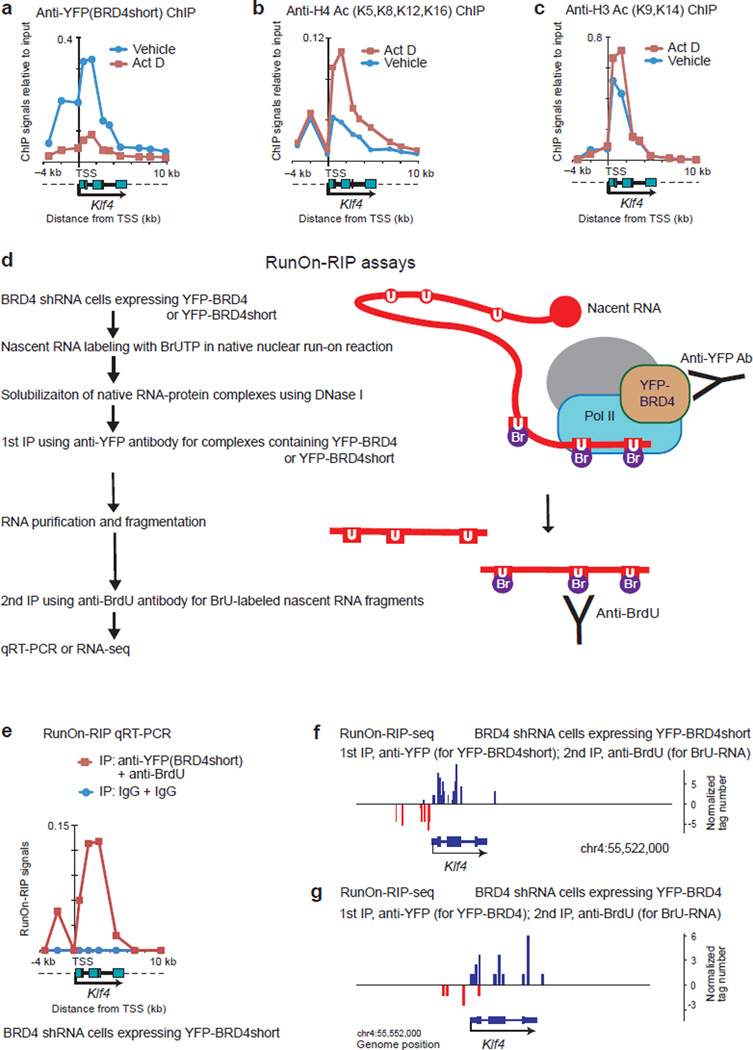
Figure 7. BRD4 interacted physically with Pol II elongation complexes in vivo.
(a–c) ChIP assays for YFP-BRD4short (a), H4 Ac (tetra-acetylated at K5, K8, K12 and K16) (b) and H3 Ac (di-acetylated at K9 and K14) (c). BRD4-knockdown cells expressing YFP-BRD4short were treated with actinomycin D (Act D, 2 µg/ml) or vehicle (DMSO) for 2 h. d, Workflow of RunOn-RIP (run-on RNA immunoprecipitation) assays for native complexes containing BRD4 and elongating RNA. Nuclei isolated from BRD4 knockdown cells reconstituted with YFP-BRD4 or YFP-BRD4short were subjected to a nuclear run-on reaction without using sarkosyl. U, uracil; BrU, bromo-uracil. The BrU-labeled, nuclear run-on transcripts were sequentially immunoprecipitated with anti-YFP antibody (for YFP-BRD4 or YFP-BRD4short) and anti-BrdU antibody (for BrU labeled RNA fragments). e, Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RunOn-RIP signals along the Klf4 gene locus. BRD4 knockdown cells reconstituted with YFP-BRD4short were analyzed. Background signals were assessed using normal rabbit IgG. (f, g) Genome browser views of RunOn-RIP-seq reads around the Klf4 gene locus, representing the actively elongating front of transcripts that were associated with YFP-BRD4short (f) or YFP-BRD4 (g).