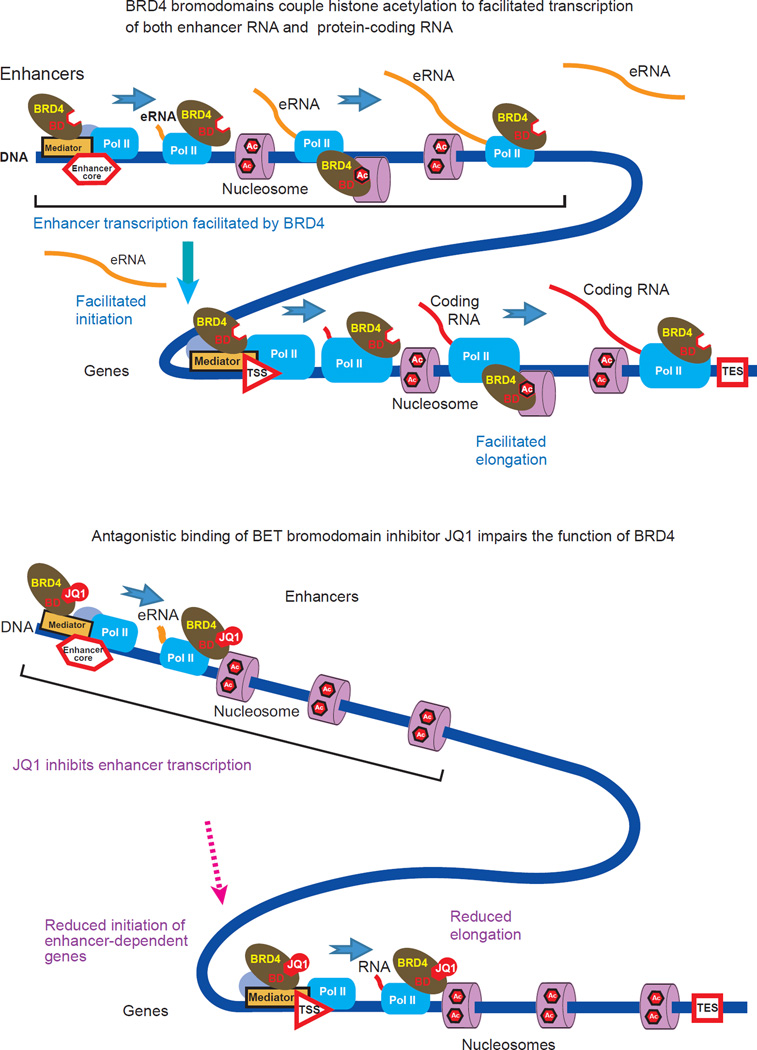
Figure 8. A model depicting the interdependence between the passage of Pol II elongation complexes through nucleosomes and acetyl-histone binding of BRD4 at enhancers and within protein-coding genes.
BRD4 contributes to the progression of the elongation complexes via its histone chaperone activity depending on its interaction with hyper-acetylated nucleosomes. The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 occludes the acetyl-histone binding pockets of the BRD4 bromodomains, disabling the elongation-facilitating activity of BRD4.