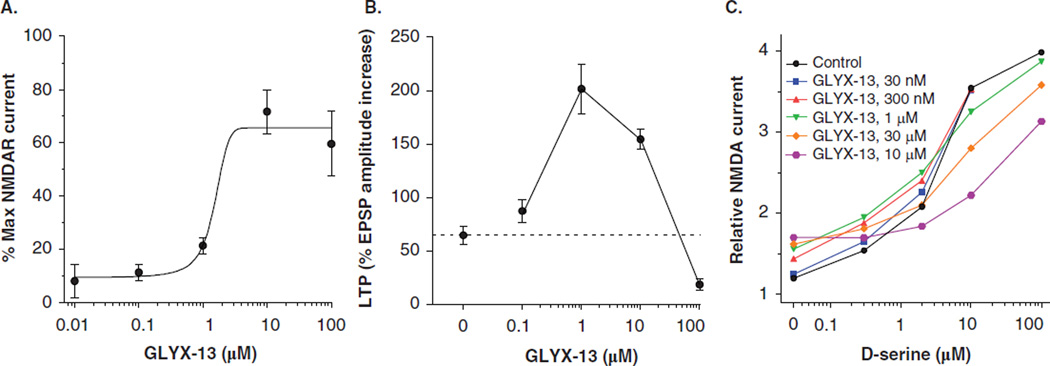
Figure 1. GLYX-13 is an NMDAR functional glycine site partial agonist.
(A) The effects of GLYX-13 on NMDA currents in oocytes. Cells were injected with e1/z1 cRNA, voltage-clamped at −80 mV in the presence of 100 µM NMDA, varying concentrations of GLYX-13, and no exogenous glycine. Data are expressed as a percentage of the current elicited by 10 µM glycine in the same cell, usually in the same trial. Results from nine cells injected with e1/z1 cRNA; error bars indicate SEM. (B) The effects of GLYX-13 (0.1 – 100 µM) on LTP induced by a high-frequency stimulus train (3 × 100 Hz/500 ms) at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses. Each point represents Mean ± SEM of normalized field EPSP slope. (C) Pharmacologically isolated NMDAR currents were recorded from whole-cell patch clamp recordings of CA1 pyramidal neurons in slices. GLYX-13 by itself (left-most symbols) elicited increased NMDAR channel current to 20% the maximum current elicited by the full-agonist D-serine. GLYX-13 added in increasing concentrations shifted the dose response of D-serine to the right. Kp = 1.3 µM was calculated using the Stephenson method [39].
Data were adapted from [29] and [33] with permission of Elsevier.