Fig. 7.
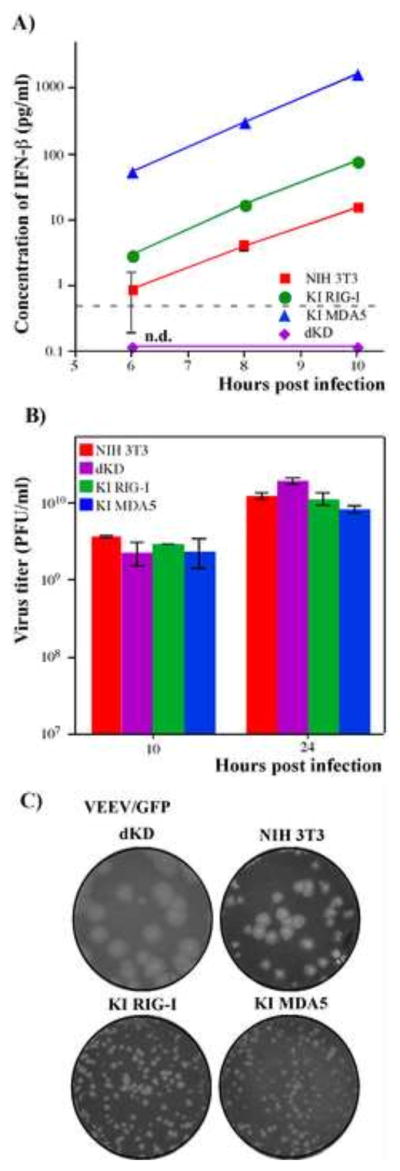
Ectopic expression of RIG-I or MDA5 in dKD cells leads to efficient IFN induction in response to replication of VEEV/GFP, which encodes wt capsid protein. (A) NIH 3T3, dKD, KI RIG-I and KI MDA5 cells were infected with VEEV/GFP at an MOI of 20 PFU/cell, and accumulation of IFN-β in the media was assessed at the indicated time points. Means of three biological repeats with SD are presented. (B) NIH 3T3, KI RIG-I, KI MDA5 and dKD cells were infected with VEEV/GFP at an MOI of 20 PFU/cell. Media were replaced at the indicated time points and titers were determined by plaque assay on BHK-21 cells. Means of three biological repeats with SD are presented. (C) NIH 3T3, KI RIG-I, KI MDA5 and dKD cells were seeded into 6-well Costar plates at a concentration of 5×105 cells per well. VEEV/GFP virus stock was serially diluted and used for infection of indicated cells with different numbers of PFUs. After 1 h incubation at 37°C the virus-containing media were replaced with 2 ml of media supplemented with 0.6% agarose. After incubation at 37°C for 48 h, cells were fixed and stained with Crystal Violet. Images represent wells infected with the same numbers of PFUs.
