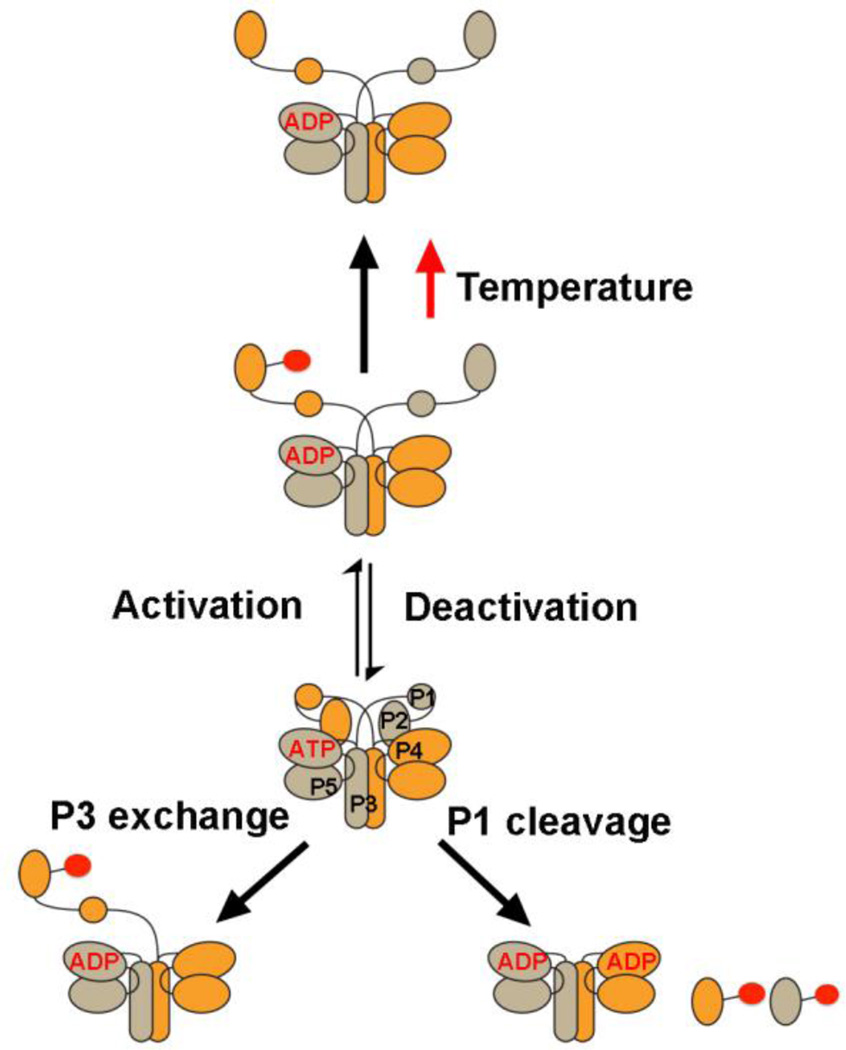
Figure 7. CheA conformational states.
The P1 substrate domain is constrained within the core CheA kinase. Activation by MCPs causes release of P1 allowing access to P4 of the adjacent subunit. Perturbations close to the ATP binding pocket trigger release. Detachment of P1 from the kinase core stimulates phosphotransfer, as does removal of one P1 domain from a CheAFL dimer. At physiological temperatures, P1-P is destabilized in a manner that also depends on the P1 domain of the adjacent subunit.