Figure 3. Neural Pathways of Fear Learning.
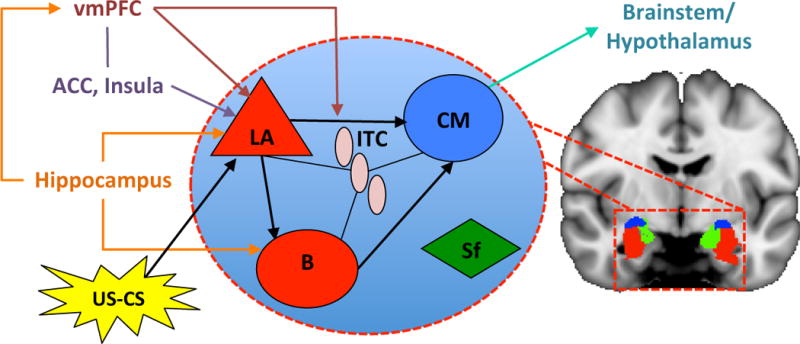
In fear conditioning, an emotionally neutral conditioned stimulus (CS; e.g., movement) is presented with an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US; pain). The CS and US converge at the lateral nucleus (LA). The LA then connects with the centromedial nucleus (CM), controlling the expression of the conditioned fear responses (CR) in the brain stem and hypothalamus. Projections from the hippocampus to the basal nucleus (B) of the amygdala process contextual information during conditioning, while the insula and anterior cingulate (ACC) influence threat encoding. During extinction learning, inhibitory connections between the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and intercalcated (ITC) cell masses are established. During extinction recall, these connections inhibit fear expression through projections to the CM. Inhibitory connections between the vmPFC and LA may also regulate fear expression through the CM. Contextual modulation of extinction expression is mediated by projections from the hippocampus to the vmPFC and/or LA. Adapted from[20; 53].
