Figure 5. Treatment Response from Time 1 to Time 2: Decrease in functional connectivity and pain-related fear.
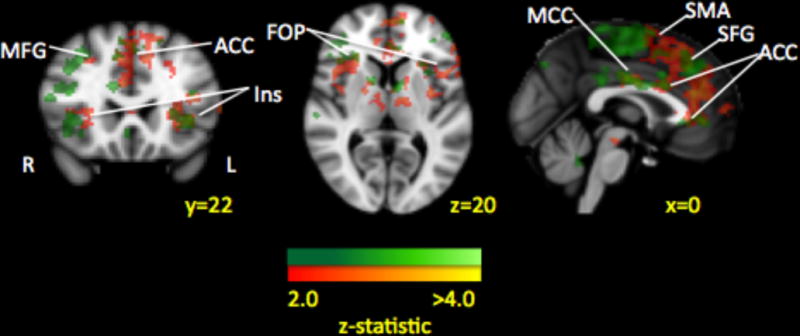
Paired analysis of amygdala connectivity changes within patients is depicted in green while connectivity changes that correlated with changes in pain-related fear are displayed in red. Many of the amygdala connectivity decreases were correlated with decreases in pain-related fear after treatment, suggesting that changes in intrinsic brain functional connectivity can be linked to symptom improvement. Key: MFG: middle frontal gyrus; Ins: insula; SMA: supplementary motor area; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; MCC: middle cingulate cortex; FOP: frontal opercular cortex.
