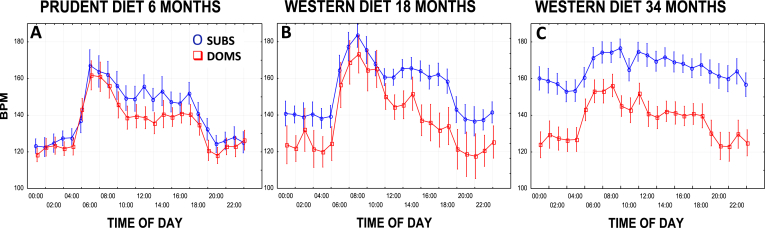
Fig. 3.
Diet, Social Status, and Autonomic Function. 24 h heart rates (HRs) were collected via telemetry from 42 socially housed monkeys at 3 time points: after consuming a low-fat plant-based prudent diet (monkey chow) for 6 months, and after consuming a Western diet for 18 and 34 months. A: Subordinate HRs were higher on average while consuming the prudent diet but not statistically different (p = 0.34); B, C: Social status differences emerged with time consuming the Western diet (main effect of social status B: 18 months p = 0.13, C: 34 months p = 0.002). C. Subordinates also lost much of their HR circadian rhythm by 34 months (C: time × status interaction p = 0.005). Sub = Subordinate; Dom = Dominant.