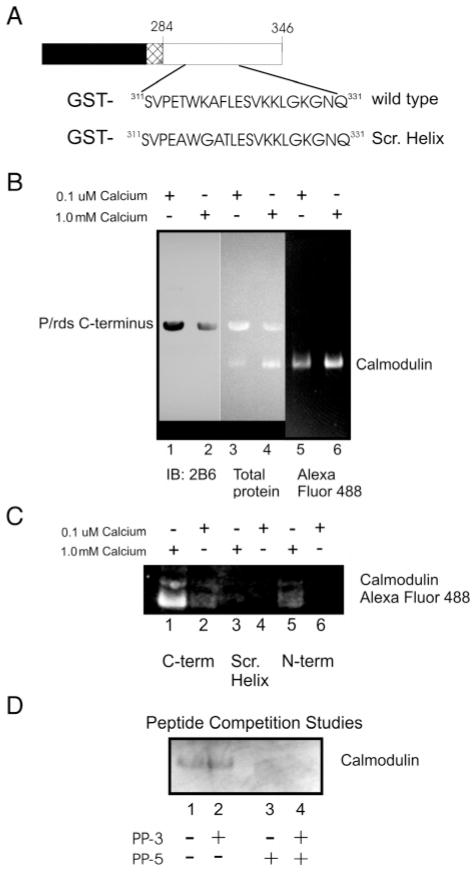
Figure 5.
Association of the p/rds C-terminus with Ca2+/CaM. (A) Schematic diagram showing the organization of the GST-p/rds polypeptides. (B) GST-PerCter fusion protein attached to glutathione resin incubated with Alexa Fluor 488CaM at 4 °C overnight as detailed in Materials and Methods in the presence of 0.1 μM calcium (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or 1.0 mM calcium (lanes 2, 4, and 6). (C) CaM does not associate with the mutant peripherin/rds C-terminus containing a scrambled helical domain (Scr. Helix). The GST-PerCter WT or Scr. Helix as well as a GST-PerNter (see Table 1) fusion protein were attached to glutathione resin and incubated with Alexa Fluor 488CaM at 4 °C overnight as detailed in Materials and Methods in the presence of 0.1 μM calcium (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or 1.0 mM calcium (lanes 2, 4, and 6). (D) Peptide corresponding to the p/rds helical fusion domain, PP-5 (V311–L325), inhibits CaM association with the PerCter. Prior to CaM addition to the immobilized GST-PerCter polypeptide, CaM was preincubated with 1.0 mM PP-5, 1.0 mM PP-3 (Q331–E346), or an equimolar mixture of the two peptides (final peptide concentration = 1.0 mM) as indicated in the Figure. GST-pull down assays were then performed essentially as described. Samples were concentrated and proteins analyzed on 12% SDS–PAGE and by Western blotting. Gels were visualized on a Kodak Image Station 440 CF using a conventional FITC filter. Western blots were probed with mouse monoclonal anti-p/rds antibody, mAb 2B6 (from Dr. R. Molday), or mouse monoclonal anti-CaM antibody.