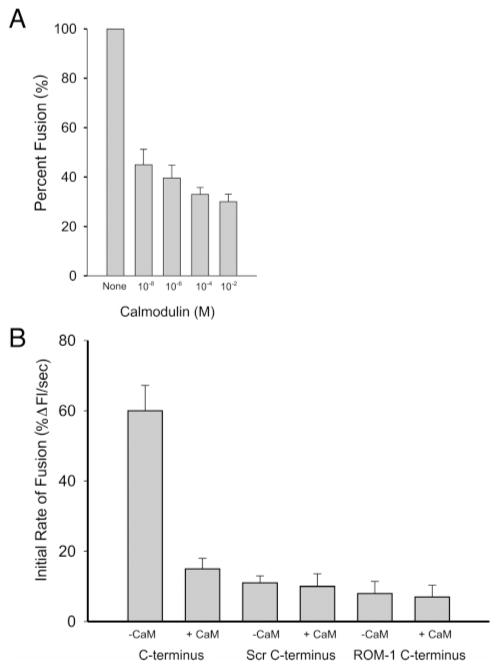
Figure 7.
Calmodulin inhibits disk-plasma membrane cell free fusion and p/rds C-terminal domain-dependent fusion. (A) Fusion between R18-labeled ROS plasma membrane vesicles and unlabeled disk membranes measured by fluorescence dequenching at 37 °C as described in Materials and Methods. Prior to the initiation of fusion, disk membranes (final phospholipid phosphate concentration of 1 uM) were preincubated for 15 min with CaM, at the concentrations indicated, and 1 mM calcium. Total fusion was calculated on the basis of fluorescence emission and normalized to disk membranes with no added Ca2+/CaM. Data are presented as a percentage of this value. (B) Purified C-terminal polypeptide promotes an NBD-PE and Rh-PE lipid mixing. The assessment of the fusogenic function of full-length C-terminal polypeptide is shown. Lipid mixing was detected using resonance energy transfer between NBD-PE and Rh-PE and was quantitated as the initial rate of fusion (IRF), % change in fluorescence intensity per second at 37 °C ± SEM, and n = 3. Fusion was initiated with the addition of GST-PerCter (C-terminus), the GST-Scr. Helix (Scr C-terminus), and a ROM-1 C-terminal polypeptide (ROM-1 C-terminus). In some experiments, the polypeptides were preincubated with 1 μM CaM (+CaM). The phospholipid to polypeptide ratio was 50–60:1.