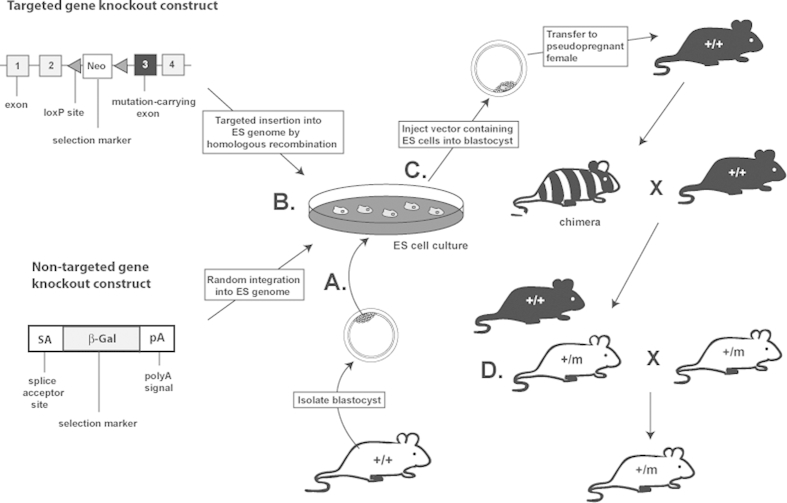
Fig. 1.
Gene knockout methods using embryonic stem (ES) cells. A Totipotent ES cells are isolated from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst from a wild type mouse and cultured. B Targeted or non-targeted vectors are introduced into the genome of the ES cells. ES cells in which homologous recombination or random integration and i.e. gene knockout, has occurred are selected using incorporated markers (e.g. Neo). C Selected ES cells are injected into a blastocyst obtained from a different strain to that in step A, and implanted into a pseudopregnant female, which is the same strain as the injected blastocyst. This results in chimeric offspring containing genetic information from both the manipulated ES cells of the original mouse strain and genetic information of the second blastocyst/pseudopregnant female of a different strain. To generate offspring heterozygous for the gene knockout, chimeric offspring are bred with wild type mice. D Heterozygous offspring can be interbred to generate homozygous knockout mice. m-mutated allele; + – wild type allele.