Figure 2. Vaccination of chickens with M2e5x VLP alone induces virus-specific antibodies but does not confer protection against HPAI virus.
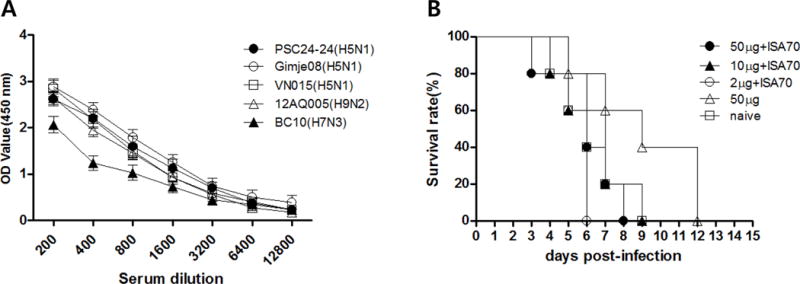
Antibody responses specific for inactivated purified virions were determined by ELISA in vaccinated and naïve chickens at 3 weeks after boost vaccination. (A) Antibody binding to purified virions. Results are expressed as the mean titer ± SD (serial dilutions, 1:200–12800) in sera from five chickens immunized with 10 μg M2e5x VLP containing ISA 70. (B) Survival of chickens after HPAI challenge. Immune and naïve groups were intranasally challenged with a lethal dose (5 × CLD50) of the A/mandarin duck/Korea/PSC24-24/2010 (H5N1) strain 3 weeks after the booster vaccination. Survival was monitored from 0 to 14 days post-infection. OD, optical density; PSC24-24, A/mandarin duck/Korea/PSC24-24/2010 (H5N1) strain; Gimje08, A/chicken/Gimje/2008 (H5N1) strain; VNA015, A/chicken/Vietnam/NCVD-A015/2008 (H5N1) strain; BC10, A/duck/Korea/BC10/07 (H7N3) strain; 12AQ005, A/Korean native chicken/Korea/12AQ005/2012 (H9N2) strain; 50 μg + ISA 70: 50 μg M2e5x VLPs containing ISA 70; 10 μg + ISA 70: 10 μg M2e5x VLPs containing ISA 70; 2 μg + ISA 70: 2 μg M2e5x VLPs containing ISA 70; 50 μg: 50 μg M2e5x VLPs without ISA 70; naïve: control group injected with PBS.
