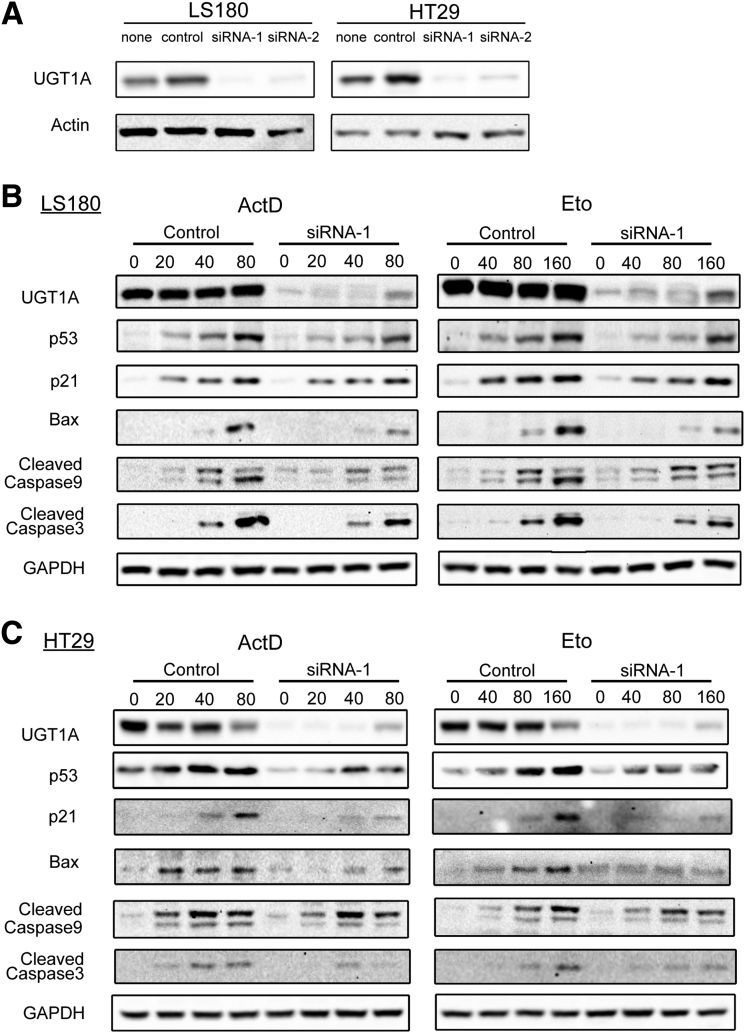
Figure 1.
UGT1A silencing inhibits actinomycin D and etoposide-induced p53 protein expression and the P53-dependent apoptosis pathway in LS180 and HT29 colon epithelial cells. (A) Assessment of gene-silencing efficiency for the two pairs of UGT1A siRNAs (siRNA1, siRNA2). Cells were treated with UGT1A-specific siRNA or nonspecific siRNA for 48 hours, and protein expression levels were examined by Western blot analysis. The cell sample without any treatment was indicated as “none” and treated with nonspecific siRNA was indicated as “control.” (B) Protein expression of p53 and genes regulated by p53. LS180 cells and HT29 cells (C) were pretreated with UGT1A-specific siRNA or non-specific siRNA for 48 hours and then incubated with actinomycin D (ActD, 20, 40, 80 nM) or etoposide (Eto, 40, 80 160 μM) for 36 hours. Whole cell lysates were prepared and expression of UGT1A, p53, p21, Bax, cleaved caspases-9, and cleaved caspases-3 were examined by Western blots. These represent an example taken from 3 independent experiments, where combined expression levels are quantitated in Supplementary Figures 1A and 1B.