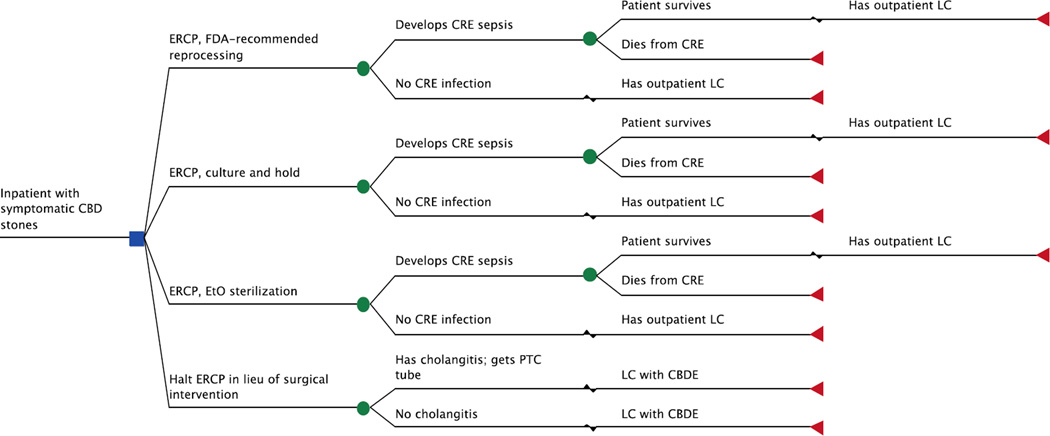
Figure 1.
Truncated decision model. The base-case patient was hospitalized with symptomatic CBD stones and underwent 1 of 4 competing strategies. The model accounted for procedure-related complications and mortality. Patients who had an ERCP were at risk for acquiring CRE; those who did not develop an overt CRE infection had an outpatient LC 6 weeks after their initial hospitalization. Those who developed CRE sepsis consequently required readmission to the hospital; patients who survived were discharged and had an outpatient LC 6 weeks later. For the surgery-based approach, treatment was stratified by presence of cholangitis, as those with cholangitis first had PTC tube placement prior to LC with CBDE.
CBD = common bile duct; CBDE = common bile duct exploration; CRE = carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; ERCP = endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EtO = ethylene oxide; FDA = Food and Drug Administration; LC = laparoscopic cholecystectomy; PTC = percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography.