Abstract
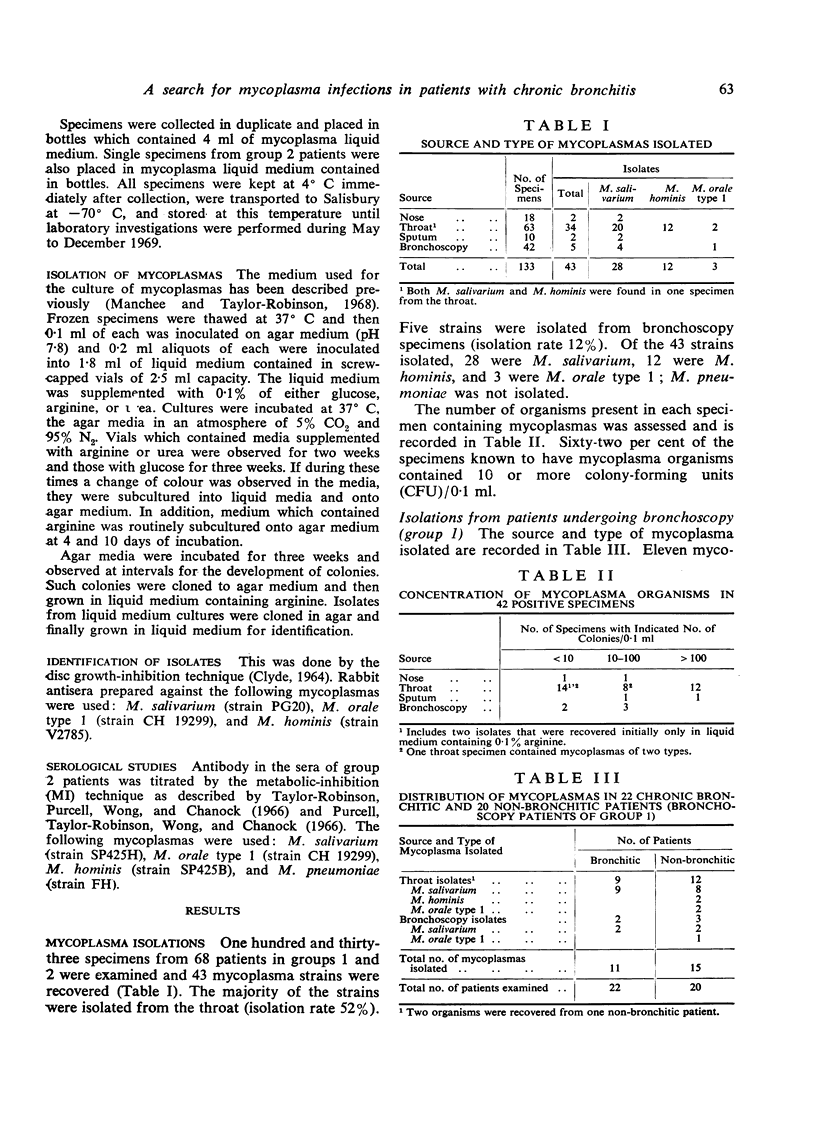
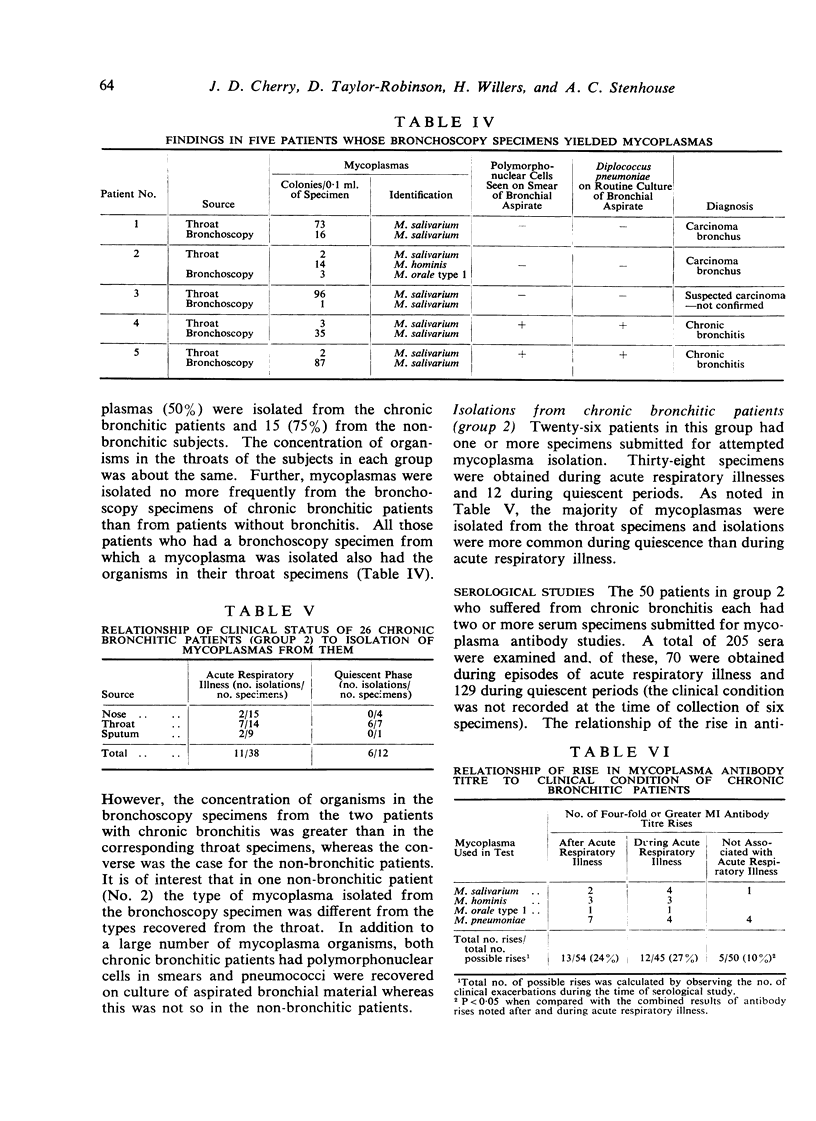
Throat and bronchoscopy specimens for mycoplasma isolation studies were collected from 22 patients with chronic bronchitis and 20 patients without chronic bronchitis. Twenty-six of 50 patients attending a chronic bronchitis clinic had throat, nasal, or sputum specimens collected for attempted mycoplasma isolation, and all of these patients had multiple serum samples taken for mycoplasma antibody studies. Mycoplasmas were recovered from throat and bronchoscopy specimens of the chronic bronchitic and non-bronchitic patients with about equal frequency. The concentration of organisms in the bronchoscopy specimens of two patients with chronic bronchitis was greater than in their throat specimens, suggesting downward spread and multiplication of mycoplasmas rather than contamination by passage of the bronchoscope. Eighty-three per cent of the rises in mycoplasma antibody titre in chronic bronchitic patients occurred during or immediately after an acute respiratory illness, and this relationship of rise in antibody titre to acute illness was significantly more frequent than rises in antibody titre not associated with illness. We suggest that mycoplasmas may be present in the bronchi of some patients suffering from chronic bronchitis and that, while such mycoplasma infections are often silent, they may become sufficiently active during infection by other agents to stimulate a mycoplasma antibody response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addey J. P., Taylor-Robinson D., Dimic M. Viability of mycoplasmas after storage in frozen or lyophilised states. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):137–145. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARILLI A. D., GOHD R. S., GORDON W. A VIROLOGIC STUDY OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Jan 16;270:123–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196401162700303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHODOSH S., SEGAL M. S. CHRONIC BRONCHITIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 23;270:894–CONTD. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196404232701709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Jordan W. S., Jr Mycoplasma pharyngeal flora in civilians. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Apr;97(4):524–532. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.4.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers J. F., Masurel N. Infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae in civilians in the Netherlands. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):447–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEES A. W., MCNAUGHT W. Bacteriology of lower-respiratory-tract secretions, sputum, and upper-respiratory-tract secretions in "normals" and chronic bronchitics. Lancet. 1959 Dec 19;2(7112):1112–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert H. P. Antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in normal subjects and in patients with chronic bronchitis. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Jun;66(2):185–189. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. E., SMITH P. F., KELLER R. Prevalence of pleuropneumonia-like organisms and the evaluation of media and methods for their isolation from clinical material. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1952 Aug;42(8):913–925. doi: 10.2105/ajph.42.8.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Haemadsorption and haemagglutination by mycoplasmas. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):465–478. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Organick A. B., Worman L. W. Isolation and identifiction of mycoplasma from the lower respiratory tract in bronchoscopy patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Apr;95(4):618–622. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A color test for the measurement of antibody to the non-acid-forming human Mycoplasma species. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jul;84(1):51–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D., Chanock R. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Canchola J., Valdesuso J. Significance of antibody to mycoplasma as measured by metabolic-inhibition techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):664–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTEL M. W., CONNER G. H., WELCH C. C., KRAYBILL W. H., EDWARDS E. A., ROSENBAUM M. J., FRANK P. F., MILLER L. F. INFECTIOUS AGENTS ASSOCIATED WITH CYLINDRICAL BRONCHIECTASIS. Dis Chest. 1964 Jul;46:23–28. doi: 10.1378/chest.46.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., McMichael S., Eadie M. B., Lees A. W., Murray E. A., Pinkerton I. Infective agents and chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1966 Sep;21(5):461–464. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.5.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMMERVILLE R. G. RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS IN ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS. Lancet. 1963 Dec 14;2(7320):1247–1248. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90894-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK J. E., HEATH R. B., CURWEN M. P. INFECTION WITH INFLUENZA AND PARAINFLUENZA VIRUSES IN CRONIC BRONCHITIS. Thorax. 1965 Mar;20:124–127. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. J., Grist N. R., Eadie M. B. Rhinovirus infections in chronic bronchitis: isolation of eight possibly new rhinovirus serotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):109–117. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenhouse A. C. Rhinovirus infection in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis: a controlled prospective study. Br Med J. 1967 Aug 19;3(5563):461–463. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5563.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


