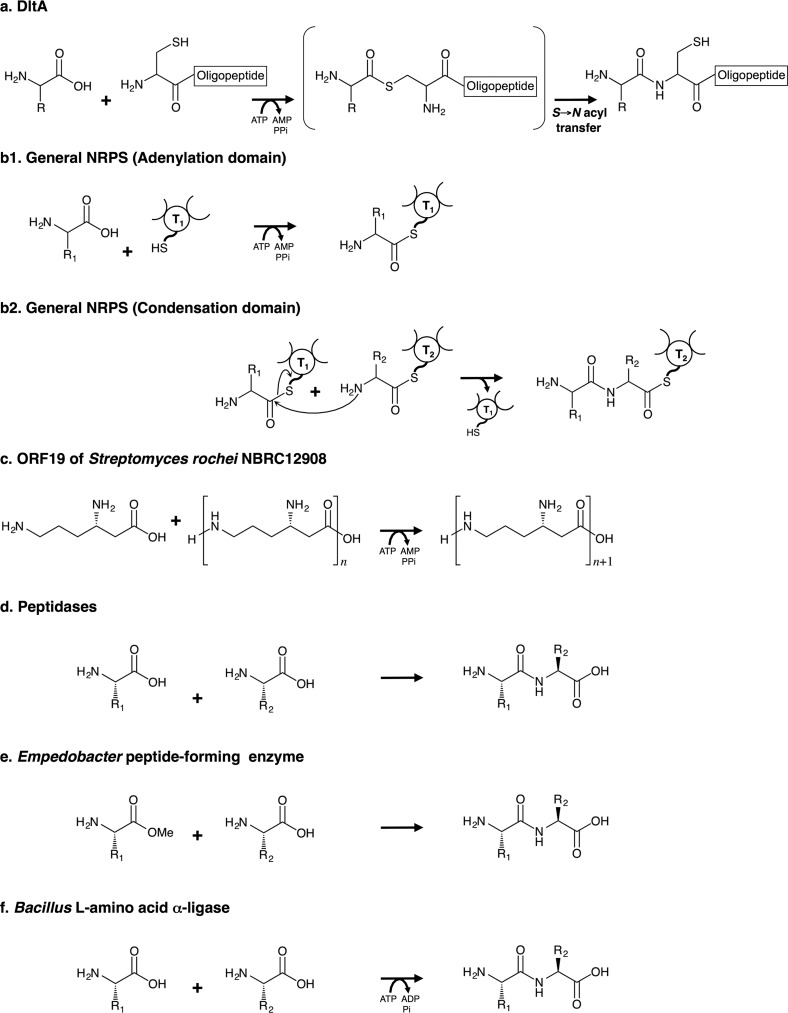
FIGURE 15.
Comparison of enzyme reactions involved in peptide/amide bond synthesis. a, oligopeptide synthesis by DltA. b1 and b2, peptide synthesis by the general NRPS system. The adenylation domain produces an S-aminoacyl-thiolation domain intermediate (b1). The reaction for peptide bond formation between two aminoacyl substrates bound to the thiolation domain proceeds under the catalytic control of the condensation domain (b2). T, 4′-Phosphopantetheine-bound thiolation domain. c, amide synthesis by ORF19 of S. rochei NBRC12908 (the stand-alone adenylation domain). ORF19 catalyzes amide bond formation only between l-β-lysine and an l-β-lysine oligopeptide. d, peptide synthesis through the reverse reaction of various peptidases. e, dipeptide synthesis by Empedobacter peptide-forming enzyme. This enzyme uses amino acid methyl esters as substrates. f, dipeptide synthesis by Bacillus l-amino acid α-ligase. This enzyme has been reported to belong to the ATP-dependent carboxylate-amine/thiol ligase superfamily.