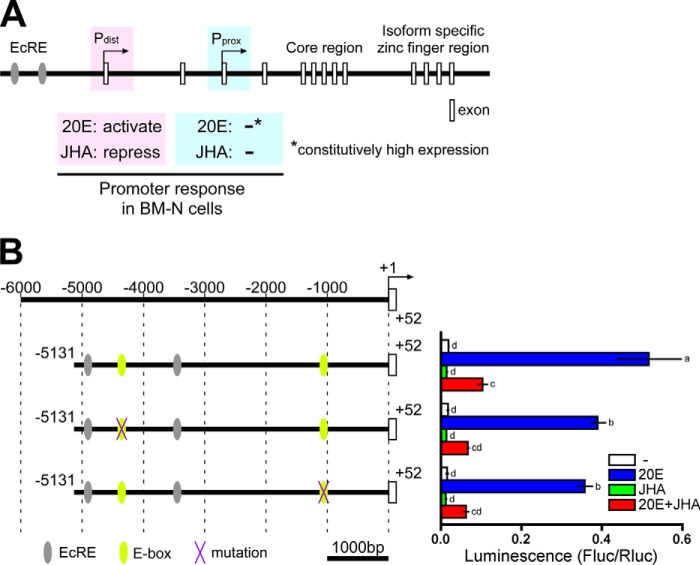
FIGURE 1.
Genomic structure of BmBR-C, hormonal responses of its promoter with reference to its E-box sequences. A, schematic representation of the genomic structure of BmBR-C. Predicted exons are shown as boxes. The BmBR-C gene has two transcriptional start sites (the distal promoter (Pdist) and the proximal promoter (Pprox)). In BM-N cells, Pdist was activated by 20E via two ecdysone response elements (EcRE; gray ellipses), and the activation was repressed by JHA, whereas the Pprox transcript was constitutively highly expressed regardless of 20E and methoprene (JHA) (40). B, functional characterization of the E-box sequences in BmBR-C_Pdist. Yellow ellipses indicate two E-box sequences (−4362 to −4357 and −1066 to −1061) located in the upstream region of BmBR-C_Pdist (−5131 to +52). Purple X marks indicate mutations of E-box sequence. BM-N cells were cotransfected with reporter plasmids that express firefly luciferase (Fluc) under the regulation of the regions indicated in the figure (−5131 to +52) and a reference reporter plasmid carrying Renilla luciferase (Rluc). Cells were treated with 1 μm 20E and/or 10 μm methoprene (JHA) for 2 days. Reporter activities were measured using a dual-luciferase reporter assay system. Data represent the means ± S.D. (n = 3). Bars with the same letter are not significantly different (Tukey-Kramer test, α = 0.05).