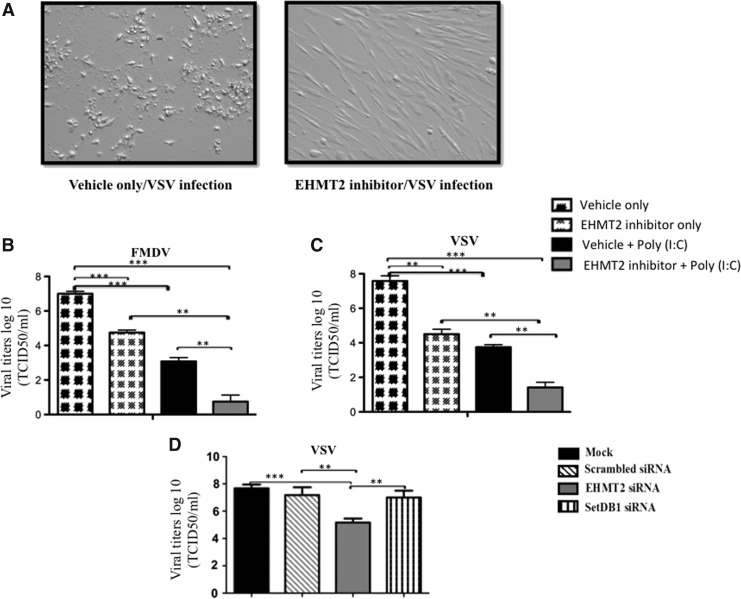
FIG. 4.
Pharmacological inhibition or depletion of EHMT2 confers protection in bovine cells against foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infections. FBF cells were treated with the EHMT2 inhibitor (5 μM) or vehicle for 4 days. Treated cells were unstimulated or stimulated with poly (I:C) (0.5 μg/mL) for 6 h, followed by infection with VSV or FMDV [multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 0.01]. Supernatants were collected at 36 or 41 hours postinfection (hpi) for determining viral titers (TCID50). For depletion of EHMT2, FBF cells were mock transfected or transfected with siRNAs targeting bovine EHMT2 or SetDB1 for 48 h followed by infection with VSV. Thirty-six hours later, supernatants were collected for determining viral titers (TCID50) in MDBK cells. (A) Left panel represents control FBF, exhibiting cytopathic effects (CPE). Right panel represents EHMT2 inhibitor-treated FBF monolayer. (B–D) Represents VSV and FMDV titers. Viral titers (log10) expressed as TCID50 per milliliter. The data (mean ± SE) are from 3 independent experiments done in duplicates. **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001 determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test.