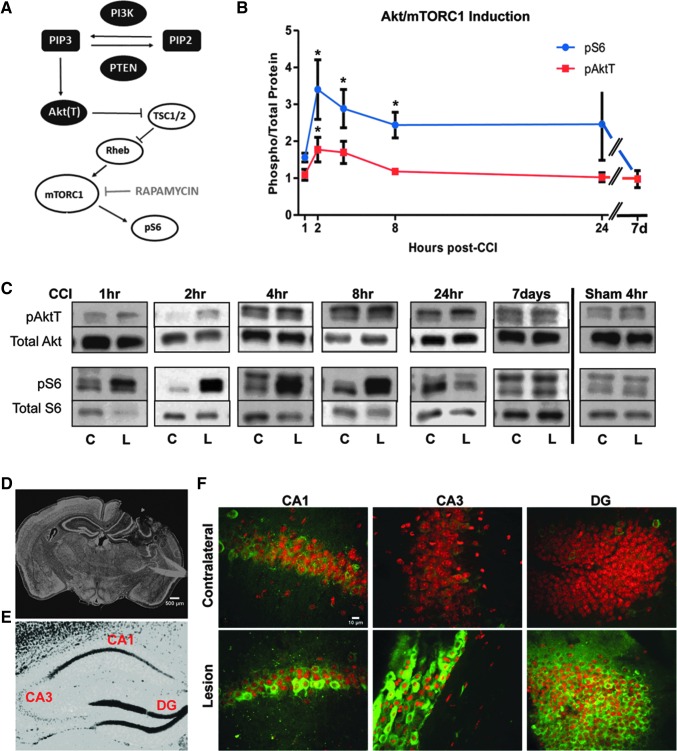
FIG. 1.
Induction of the Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway by controlled cortical impact (CCI). (A) Diagram of the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 signaling cascade. (B) Time course of phosphorylation of Akt (pAktT) and S6 (pS6) proteins in the hippocampus after CCI. Values indicate the average ratio of phosphoryated/total proteins in the lesion side relative to the contralateral side of each injured brain (*p < 0.05 by analysis of variance). (C) Representative Western blot data showing the levels of phosphorylated and total Akt and S6 proteins at each time point in the lesion (L) and contralateral (C) side after CCI or sham surgery. (D) Representative low magnification image of a whole brain section after CCI. The section was stained with SYTOX nuclear stain. (E) Sample image of the hippocampus showing the location of regions of interest, such as area CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG). (F) High magnification (20x) confocal images of the CA1, CA3, and DG regions in the C and L side of the brain after CCI. Sections were stained with fluorophore-conjugated anti-pS6 antibody (green) and Reddot 2 nuclear stain. Scale bars: 500 μm (D) and 10 μm (F). Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu