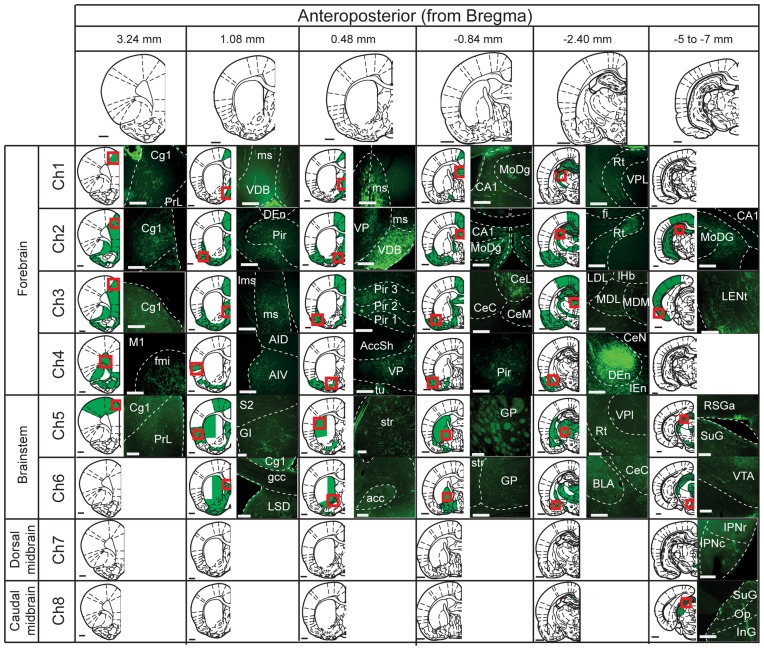
Figure 2.
Mapping of cholinergic axons. Six representative coronal sections (anterior and posterior to bregma; columns) were selected to map the projections of the cholinergic neurons in the different cholinergic nuclei (Ch1 to Ch8; rows). For each cholinergic cell group, the rows depict schematic summaries where green shaded areas indicate high density of fluorescently-labeled axons. Red squares indicate the site where the fluorescent images on the right were obtained. Abbreviations (if not defined previously): Accsh, nucleus accumbens shell; AccC, nucleus accumbens core; AID, agranular insular dorsal cortex, AIV, agranular insular ventral cortex; BLA, basolateral amygdala; CA1, CA1 field of the hippocampus; CE, central amygdala (L, lateral; M, medial; C, capsular); Cg, cingulate cortex; Den, dorsal endopiriform nucleus; fmi, external capsule; GI, granular insular cortex; gcc, genu of the corpus callosum; GP, globus pallidus; IEn, intermediate endopiriform nucleus; InG, intermediate gray layer superior colliculus; IPN, interpeduncular nucleus (c, caudal; r, rostral); LDL, laterodorsal thalamic nucleus lateral part; LENt, lateral enthorinal cortex; Lms, lateral septum; LSD, lateral septum dorsal part; M, motor cortex; MD, mediodorsal thalamic nucleus (M, medial; L, lateral); MoDG, molecular layer dentate gyrus; Op, optic nerves layer superior colliculus; Pir, piriform cortex; PoDg, polymorph layer dentate gyrus; RSGa, retrospinal granular cortex; Rt, reticular thalamic nucleus; S, somatosensory cortex; SuG, superficial gray superior colliculus; VP, ventral pallidum; VPL, ventro-posterior thalamic nucleus lateral part; VTA, ventral tegmental area. Scale bars: brain outlines, 1000 μm; fluorescent images, 200 μm.