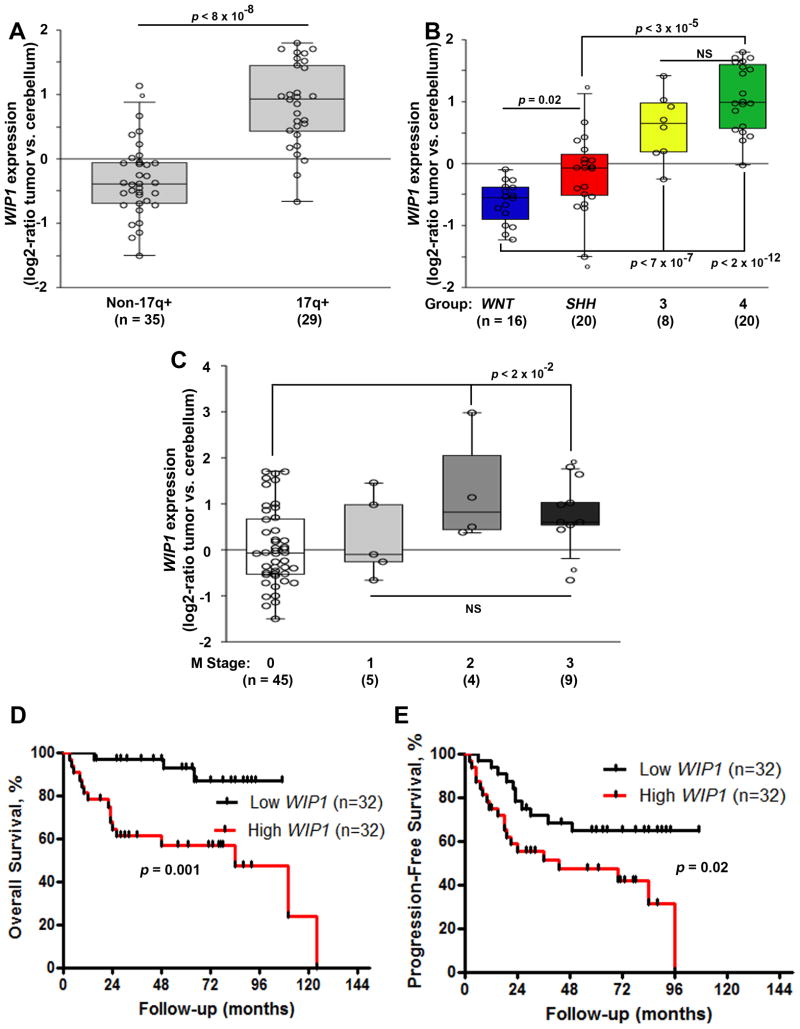
Figure 1. High WIP1 expression in medulloblastoma is associated with adverse prognostic factors and inferior survival.
(A) WIP1 expression, based on gene expression profiling, in 64 pediatric medulloblastomas, with or without gain of chromosome 17q. Copy number status of chromosome 17q was determined using an Agilent-014850 Whole Human Genome Microarray 4×44K G4112F and array-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). (B) WIP1 expression among medulloblastoma subgroups. Subgroup affiliation was determined using unsupervised clustering approaches. (C) WIP1 expression, segregated by Chang M stage. R2 software was used to compare WIP1 expression according to 17q status, subgroup, and M stage. (D, E) Kaplan-Meier analysis of patient survival was based on median WIP1 expression. Survival was measured from diagnosis until death or last follow-up. Patient survival was analyzed according to the Kaplan-Meier method, using log-rank statistics. The median value, in panels A-C, is denoted by the middle line in each rectangle. Whiskers represent the bottom 10th and top 90th percentiles. The Y-axis denotes relative expression (log2-ratio tumor vs. cerebellum controls). NS, not significant.