Fig. 1.
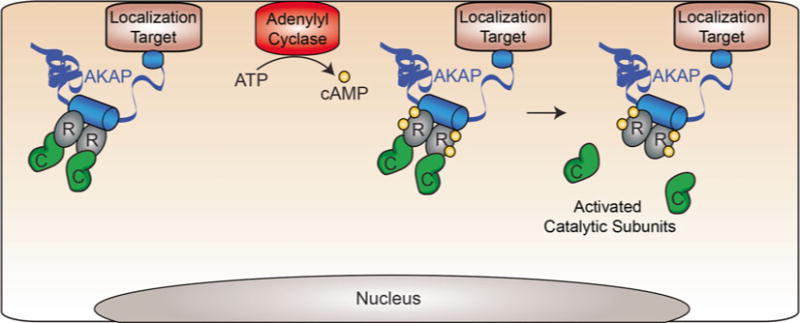
Signaling through AKAP complexes. When intracellular concentrations of cAMP are low, the PKA holoenzyme complex is largely bound to AKAPs within the cell. AKAPs are localized to various intracellular sites including the plasma membrane and organelles, thereby concentrating PKA to particular locations within the cell. Upon stimulation, intracellular cAMP levels rise. Each R-subunit of PKA binds two cAMP molecules and undergoes an allosteric conformational change to release the activated catalytic subunits
